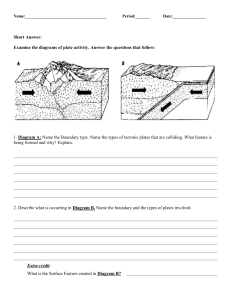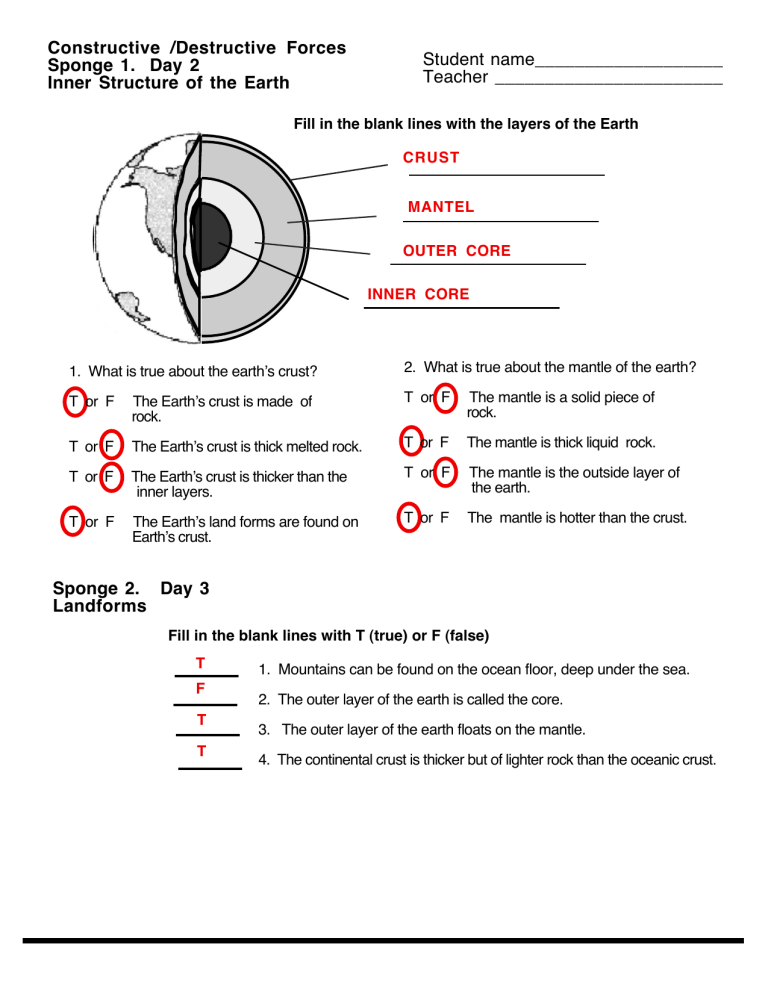
Constructive /Destructive Forces Sponge 1. Day 2 Inner Structure of the Earth Student name___________________ Teacher _______________________ Fill in the blank lines with the layers of the Earth CRUST MANTEL OUTER CORE INNER CORE 1. What is true about the earthʼs crust? 2. What is true about the mantle of the earth? T or F The Earthʼs crust is made of rock. T or F The mantle is a solid piece of rock. T or F The Earthʼs crust is thick melted rock. T or F The mantle is thick liquid rock. T or F The Earthʼs crust is thicker than the inner layers. T or F The mantle is the outside layer of the earth. T or F The Earthʼs land forms are found on Earthʼs crust. T or F The mantle is hotter than the crust. Sponge 2. Day 3 Landforms Fill in the blank lines with T (true) or F (false) T F T T 1. Mountains can be found on the ocean floor, deep under the sea. 2. The outer layer of the earth is called the core. 3. The outer layer of the earth floats on the mantle. 4. The continental crust is thicker but of lighter rock than the oceanic crust. 5. Draw lines connecting the picture with the correct definition and then to the name. Use the mountain range as an example of how to do the rest. ICE A large stream of water usually emptying into a lake or the ocean. A river A flat area of rock with steep sides smaller than a plateau. A cave A long narrow valley with steep sides. A valley A large mass of ice that flows over land. A volcano A very large hole or open space underground or in the side of a cliff A glacier An opening in the Earthʼs surface through which melted rock, ash and gases can flow out of the inside of the Earth. A Canyon A group of mountains close to one another. A mountain range A long lowland between mountains or hills. A mesa Sponge 3. Day 4 More Landforms 1. As in your sand box landscape, this drawing shows many of the landforms we are learning about. From the word bank, write the name of each landform by the arrow that points to it. MOUNTAINS GLACIER HILLS CANYON VALLEY RIVER WORD BANK DELTA ISLAND Hills Mountains Glacier Canyon Ocean Valley Delta Island River OCEAN Sponge 4. Day 5 Earthʼs crust 1. What does this map show about the Earthʼs crust? a. that the Earthʼ s surface is flat b. that the Earthʼs crust is a solid c. that the Earthʼs crust is made up of big pieces of rock called plates d. how the ocean currents move 2. The arrows show a. the direction the plates move b. the direction the winds blow c. the direction the ocean currents move d. lines of longitude on a map of the Earth 3. Which of these drawings of plates shows them pushing into each other? (circle the correct choice) a. b. c. Sponge 5. Day 6 More Earthʼs crust 1. Mark true or false T or F The Earthʼs crust is made up of huge solid rock pieces called plates. T or F The Earthʼs crust is made of molten (melted ) rock called magma. T or F The plates of the Earthʼs crust float on molten (melted) rock called magma. T or F T or F T or F The plates of the Earthʼs crust move around slowly. The plates of the Earthʼs crust never move. The plates of the Earthʼs crust sometimes very slowly push together. T or F The plates of the Earthʼs crust sometimes move away from one another. T or F The molten rock in the mantle can never break though the crust. T or F When there is a hole or crack in the crust of the Earth the molten rock in the mantle comes to the surface and hardens into solid rock. When magma flows onto the surface of the Earth, it is called lava. T or F 2. The plates of the Earthʼs crust move in three ways. Label the diagrams below that show the ways that places can move. . Two plates can MOVE APART Two plates can SLIDE PAST EACH OTHER Two plates can PUSH TOGETHER 3.. Plate movement can cause a. volcanos, mountains and earthquakes b. floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes c. deltas and glaciers d. mesas, canyons, and plains n Sponge 6. Day 7 Earthʼs Plates 1.. The red hot, thick oozy material that lies just under the Earthʼs crust is called: a. liquid iron b. batter c. magma d. mantle 2. When two oceanic plates pull apart as shown in the diagram, what would you expect to happen? a. The ocean water would get cooler b. magma would ooze out c. a deep trench would form between the two plates d. nothing, the plates are too big to pull apart 3. What would be the result of oceanic plates pulling apart? a. The escaping magma would pile up b. The magma would cool and turn into rock c. Over a very long time mountains will build up d. all of the above are correct Sponge 7. Day 8 Earthʼs Plates 1. What is happening in this diagram? a. Two continental plates are colliding. b. The plate with lighter crust is being forced down. c. An oceanic plate is being forced under a continental plate d. Two oceanic plates are moving apart. 2. This ia a diagram showing two continental plates pushing together. Which of the following would not occur as a result. a. b. c. d. A chain of mountains will form A deep trench will form Earthquakes will occur The land on both plates+ is lifted. Sponge 8. Day 9 Review Yesterday we learned that the hands could bu used to represent the plates of the earthʼs surface. A. 1. Drawing “A” on the right is how we represented: a. b. c. d. Oceanic plates pulling apart. Two plates sliding past one another. A continental plate going under an oceanic plate. Mountains being formed as plates push together. 2. Drawing “B” on the right is how we represented: a. b. c. d. Oceanic plates pulling apart. Two plates sliding past one another. A continental plate going under an oceanic plate. Mountains being formed as plates push together. B. 3.. What do the raised thumbs in drawing “B” represent? a. b. c. d. Magma pushing up between the plates. Nothing, they are just part of the hands. They show the force that is separating the plates. Large rocks that are keeping the plates apart. 4... In drawing “C” we represent two plates sliding past one another that get hung up on something that does not let them move (our thumbs).. By continuing to push harder, we can cause the thumbs to break free. If this happened between two of Earths plates, what would likely happen? a. b. c. d. C. Volcanos. Tornados. Hurricanes. Earthquakes. 5. Drawing “D” on the right represents: a. A continental plate sliding under an oceanic plate. b. Two continental plates pushing together making mountains. c. Two oceanic plates separating causing Earthquakes. d. An oceanic plate sliding under a continental plate. 6. In drawing “D”, the finger sticking out from the left hand represents: . a. Volcanos b. Earthquakes. c. High plateaus. d. Deep canyons. D. Sponge 9. Day 10 More review 1. What is created when magma pushes through the crust and lava flows onto the land? a. b. c. d. a glacier is formed a trench is formed a continental plate is formed new land is formed. 2.. New mountains can be created when: a. When a volcano erupts at a hot spot. b. When two continents collide c. When two oceanic plates move apart and the magma oozes out or erupts from a volcano. d. All of the above. Sponge 10. Day 11 Weathering and Erosion 1 Over time, millions or even thousands, of years, the earthʼs surface is constantly changing. (True) (False) 2 New land can be created by lava flowing onto the land. Likewise, landforms can be broken down by the process of: a. Deposition b. Volcano eruptions c. Landform uplifting d. Weathering: 3. Newly formed mountains generally have sharp pointed peaks like the one shown in diagram “A”. After millions of years, these sharp peaked mountain become rounded and look more like the mountains in diagram “B”. What causes mountains as they age to become smaller and more rounded? a. earthquakes and volcanos b. weathering and erosion A. c. magma cooling on the earth surface. d. ultraviolet rays from the Sun and Moon B. 4. The breaking of rocks into smaller and smaller pieces, is the definition of: a. Deposition b. Volcano eruptions c. Landform uplifting d. Weathering: Sponge 11. Day 12 Weathering and Erosion 1. Water trapped inside cracks in rocks may freeze. Frozen water expands and can cause: a. the rocks to become harder b. the pressure of the magma under the crust to increase. c. earthquakes to occur d. rocks to break apart 2. Plants are growing in this rock. When plants, particularly trees, grow in rocks their roots cause a. b. c. d. the rock to break into smaller pieces the rocks to expand and grow bigger the rock to become smoother the rock to explode 3. At one time the land shown in the diagram was flat as in diagram A.. What has caused the change shown in diagram B? a. earthquakes occurring b. volcanos erupting Diagram A c. a river flowing over the rock d. glaciers moving over the rock Diagram B 4. What landform results in diagram B? a. Desert b. Delta c. Mountain d. Canyon Sponge 12. Day 13 Erosion 1. This diagram shows a deep canyon like the Grand Canyon. What caused the Grand Canyon to form? a. weathering and erosion by water and wind b. earthquakes c. two of Earthʼs plates separating d. deposition 2 How long did it take take for the Grand Canyon to form? a b. c. d. less than 100 years hundreds of years thousands of years millions of years Sponge 13. Day 14 To weathering and erosion, add deposition 1. Match the word with its definition: c ______ 1. weathering a. rock, soil or shell pieces carried by wind, water or ice and later deposited. b ______ 2. eroding d ______ 3. deposition a ______ 4. sediment b. moving rock pieces or soil by water, wind or ice c. the breaking down of rock into smaller pieces by wind, water or ice. d. when broken up rock or soil is dropped in a new place 2 The mouth of the Mississippi River looks something like this. Sand and soil from up stream is carried in the fast moving water, but when the water slows down, these sediments are dropped out causing a delta to form What is THE the name given to this process? a b. c. d. Deposition Weathering Erosion Watering Sea Sponge 14. Day 15 soil 1 Soil is made up of:: a. b. c. d. Weathered rock Humus (remains of dead plants and animals) Water and air All of the above. 2. What are the four main types of soil? a. sand, silt, clay & humus b. topsoil, subsoil, weathered rock, bedrock c. pebbles, gravel, sand, clay d. weathered rocks, mineral, water , air 3 On the line, arrange these 5 kinds of weathered rock from the biggest to smallest particles: clay, gravel, sand, boulders, silt 1. BOLDER * Then circle the pieces of weathered rock that are types of soil. 2. GRAVEL 3. SAND 4. SILT 5. CLAY LARGEST SIZED PARTICLES smallest sized particles Sponge 15. Day 16 observe sand, dry clay, wet clay and humus. clay humus 40 mL of water 15 mL of water 50 mL of water was added to each funnel 1. . The results of the experiment above comparing clay and sand show that : a. humus retained more water than clay b. sand dissolved in water 2. Which soil would be best for growing plants? a. b. c. d. Sand Humus Clay A mixture of sand, clay and humus c. clay retained more water than humus d. clay dissolved in water