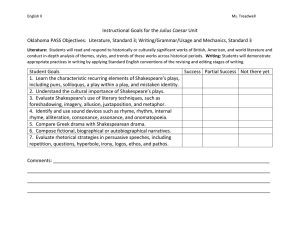
POETIC DEVICES Simile: a figure of speech involving the comparison of one thing with another thing of a different kind, used to make a description more emphatic or vivid (e.g. as brave as a lion ). While most similes use the connecting words "like" or "as" to establish the comparison they're making, similes can use other words that create a direct comparison, including other connecting words (such as, "so" or "than") or verbs of comparison (such as, "compare" and "resemble"). Metaphor: a figure of speech that makes an implicit, implied, or hidden comparison between two things that are unrelated, but which share some common characteristics (e.g. War is the mother of all battles). Personification: the attribution of a personal nature or human characteristics to something non-human, or the representation of an abstract quality in human form (e.g. The first rays of morning tiptoed through the meadow). Alliteration: the occurrence of the same letter or sound at the beginning of adjacent or closely connected words (e.g. sweet birds sang) Symbolism: the use of symbols to signify ideas and qualities, by giving them symbolic meanings that are different from their literal sense (e.g. a heart is a symbol for love or passion). Imagery: use figurative language to represent objects, actions, and ideas in such a way that it appeals to our physical senses (e.g. He whiffed the aroma of brewed coffee). Repetition: a literary device that repeats the same words or phrases a few times to make an idea clearer and more memorable (e.g. “It was many and many a year ago, In a kingdom by the sea, That a maiden there lived whom you may know … I was a child and she was a child, In this kingdom by the sea). Irony: a figure of speech in which words are used in such a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning of the words. It may also be a situation that ends up in quite a different way than what is generally anticipated (e.g. The name of Britain’s biggest dog was Tiny). Rhyme Scheme: A rhyme scheme is the pattern of rhymes at the end of each line of a poem or song. It is usually referred to by using letters to indicate which lines rhyme; lines designated with the same letter all rhyme with each other. (An example of the ABAB rhyming scheme: Bid me to weep, and I will weep While I have eyes to see And having none, yet I will keep A B A A heart to weep for thee B ) Oxymoron: a figure of speech in which apparently contradictory terms appear in conjunction (e.g. faith unfaithful kept him falsely true ). Onomatopoeia: a word which imitates the natural sounds of a thing \9e.g. splash, buzz, thump etc). Hyperbole: exaggerated statements or claims not meant to be taken literally (e.g. I have a million things to do today) Satire: Satire is a technique employed by writers to expose and criticize foolishness and corruption of an individual or a society, by using humor, irony, exaggeration or ridicule (e.g. “What’s the use you learning to do right, when it’s troublesome to do right and isn’t no trouble to do wrong, and the wages is just the same?”) Mood: a literary element that evokes certain feelings or vibes in readers through words and descriptions (e.g. gloomy, peaceful, tragic, humorous etc). TONE: the tone of a literary work is the effect that the writer creates on the readers through choice of writing style. The overall objective is to express an attitude or certain feelings about the subject matter. ASSONANCE: Assonance takes place when two or more words, close to one another repeat the same vowel sound, but start with different consonant sounds. e.g We light fire on the mountain. PUN: A pun is a joke that makes a play on words. A pun makes use of words that have more than one meaning, or words that sound similar but have different meanings, to humorous effect. The rhetorical term for punning is paronomasia, which literally means "to call a different name." e.g. I was struggling to figure out how lightning works, but then it struck me. Consonance: Consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds in the middle or end of a word. While consonance is generally used less frequently than assonance, divas (and boy bands) still utilize consonance to create catchy lyrics. e.g. Don’t pay him any attention.” The “n” sound in don’t and any Allegory. An allegory is a story that can be read in two ways: with a literal meaning on the surface, and a hidden meaning underneath that comments on a political or social situation. e.g. The Phantom Toll booth