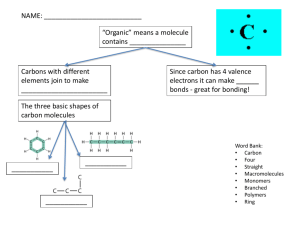
S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Bio molecules Glossary Biological molecules: Organic molecules that make up living cells. They are the cells’ building blocks. Metabolism: Sum of all the chemical reactions occurring in living cells. Catabolism: Reactions that involve breaking down molecules into smaller units. Energy is released Anabolism: Reactions by which living organisms synthesize complex molecules of life from simpler ones. Uses energy. Organic molecules: Compounds that contain carbon hydrogen bonds. Macromolecules: “giant molecules” Examples: Polysaccharides, proteins(polypeptides), and nucleic acids. Polymers: Poly means “many”. Macromolecules made of many repeating subunits that are similar or identical to each other. Monomer: The repeating subunits that make up polymers. The bio molecules are: Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids. 1_ Carbohydrates They are classified depending on the amount of sugar units that form it. The word saccharide means “sugar”: Monosaccharide: Consist of a single sugar unit (Ex: Glucose, fructose) Disaccharide: Consist of two sugar units (Ex: Maltose, sucrose) Polysaccharide: Consist of many sugar units. (Starch, glycogen, cellulose) The smaller units, or monomers, of carbohydrates are the monosaccharides. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore The most common monosaccharide is glucose (C6H12O6) but there are other sugars (fructose, for example, is the monomer that makes up sucrose, the sugar that you eat) Glucose molecule Formula: C6H12O6 Two glucose molecules can react together to form a disaccharide. The reaction is called a condensation reaction, because water is formed in the process, as shown in the diagram. The resulting bond is called: glyosidic bond. The reverse reaction (to break the bond) is called a hydrolysis reaction, and water is used. Monosaccharides and disaccharides taste sweet, they are called sugars. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Role of sugars in living organisms: Commonly used as source of energy in respiration. Also building blocks of larger molecules. If many sugars are linked together, a polysaccharide is formed. Polysaccharides don´t taste sweet. So they are NOT called sugars. Examples of polysaccharides are: Starch, glycogen and cellulose. The three are polymers of glucose. Cellulose: Makes up the cell wall of plant cells. Starch and glycogen: Very important for glucose storage. Starch is glucose storage in plants, Glycogen is glucose storage in animals. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Storage. In chloroplasts in plant cells Storage. In animals, Structure. Makes liver and muscle cells the cell wall of plant cells Because glucose is the main source of energy for many living cells, it is very important to store it. Glucose cannot be stored as a monosaccharide for two main reasons: It dissolves too easily and would make the cell content too concentrated (Osmotic problems) It is a very reactive molecule, so it would interfere with normal cell chemistry. When glucose is linked to others, to form starch or glycogen, it is not soluble and not reactive. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Starch is found in chloroplasts of Glycogen is found in liver and photosynthetic cells in plants. muscle cells of animals. In your mouth starch is digested into maltose (a sugar). Using a cracker and your mouth design an experiment to measure how long it takes for starch to be digested in your mouth: …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. Fill in the blanks: Plants produce their own glucose, by a process called_____________ The energy needed for this reaction is obtained from_______________. The elements needed to build glucose are Carbon Hydrogen and Oxygen, these elements are obtained from___________ and ___________ When a plant cell needs energy, it would obtain the ___________ needed for cellular respiration, by a _____________ reaction of __________stored in its chloroplasts. Animals, instead, need to eat the glucose. We can obtain it as sugars or as polysaccharides, such as starch. Glucose needs no digestion; it can be directly absorbed in the________ _____________. Starch needs to be digested, so that the resultant ……………………. can be absorbed. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore We have no digestive enzymes for cellulose, so the glucose in cellulose of eaten plant cells cannot be …………………….. by us. Food tests: Nutrient Reagent Positive result Negative result Sugar Benedict and double boil Green or Orange red Blue Starch Iodine Blue black Yellow brown Food source for carbohydrates. The main source of carbohydrates for humans are the foods that contain starch. Starch is used by plants as glucose storage. Seeds such as wheat have plenty of starch, other seeds that have starch are rice and maize. Cereals, in general are a very good source of starch. When wheat is powered we produce flour, so foods made with flour are a very good source of carbohydrates. Name food made with flour which are a very good source of carbohydrates: …………………………………............................... ……………………………………………………………………………………………. 2_ Proteins Are also called polypeptides. A polypeptide is a molecule made of many amino acids linked together. So proteins are long chains (polymers) of amino acids (monomers). Amino acid structure All amino acids share a basic structure, but have a part (R ) that is different There are 20 different amino acids. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Proteins differ in the amino acids that make it and their sequence (just like different words can be made by different combinations of the different letters of the alphabet) The amino acids join together by a condensation reaction. The resulting bond is called peptide bond. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore The peptide bond is very strong. It is not broken by changes in temperature or PH. To break the peptide bond a hydrolysis reaction done by enzymes is needed (such as it occurs in digestion) The types of amino acids contained in a chain, and the sequence in which they are joined makes up the primary structure of proteins. Secondary structure: The polypeptide often folds, this is due to attraction between amino acids in the chain. Tertiary structure: A protein coils to form a precise 3 dimensional shape. Quaternary structure: Many proteins are made of 2 or more polypeptide chains. All the bonds that maintain secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure can be disrupted by high temp or PH changes. Protein denaturation: A protein needs it specific 3D shape to function well. So high temp and PH changes, which break bonds that hold 2ry, 3ry structure in shape, causes the protein to go back to its primary structure. The protein is said to be denatured and is not active (not able to perform its function) S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Role of proteins in living cells: Part of cell membranes, enzymes, make up the structure, antibodies. Crucial building blocks of cells. Required for growth and repair (building new cells, muscle build up for ex) Food tests for proteins: Nutrient Reagent Positive result Negative result Protein Biuret Violet Blue Food sources for proteins: …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… Fill in the blanks How do we obtain our proteins? Probably you have heard that you need to eat proteins to grow and to be strong. In a sense this is true, BUT the proteins that you eat are NOT the ones your cells use. When you eat proteins, these are digested in the ___________ and the __________ __________, by the enzymes: ______________ . S4N. Biology Carolina Moore The resultant ________ _________ are then absorbed and travel by the blood to the cells in your body. The cell will use these amino acids to produce its own proteins. The information of the primary structure of the proteins you have to build is in the _________ of your cells. Which proteins are going to be synthesized, depends on the cell activity. For example, white blood cells produce their own antibodies, but if there are not enough amino acids, less antibodies than needed can be built. So, not eating enough proteins might cause you to become sick more often. Plants produce their own bio molecules. So, after producing glucose by photosynthesis, they transform it into the amino acids they need, so that each cell has the amino acids needed to build its own proteins. Which element, needed to synthesize amino acids is missing from glucose? _______________ How do plants obtain that missing element? _______________________________________________________________ 3_ Lipids Lipids are not polymers. Even though they are made of smaller molecules, they are not a chain of repeating units. The most common are triglycerides. They are made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids. Cell membranes are made of a bi layer of phospho lipids. Role in living organisms: Energy reserves. Insulator Fatty acids S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Triglyceride: 1 Glycerol + 3 Fatty acids 4. Nucleic acids Polymers of nucleotides. Nucleotide: Phosphate + sugar + base S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides linked to each other DNA is a double helix structure, made of two chains of nucleotides. Each chain of the double helix is joined to each other by complementary bases. S4N. Biology Carolina Moore DNA is used for making proteins. The cell “reads” the DNA and translate it into proteins S4N. Biology Carolina Moore The DNA is read in codons. Codons are like the DNA “words” each codon codes for a specific amino acid. By reading all the codons together, the cell puts the amino acids together in the correct sequence therefore building the protein primary structure, according to the cell´s DNA “instructions” S4N. Biology Carolina Moore Remarkably ALL living cells /from bacteria to complex organisms) read the DNA in the same way. They all share the same genetic code (all cells use the same “genetic” language). Discuss implications of this fact for: Common ancestor theory of evolution……………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………. Genetically modified organisms………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………. ATP: Energy currency of the cell