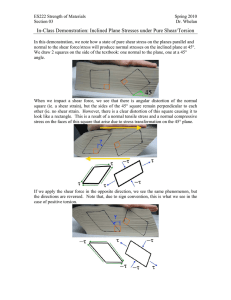
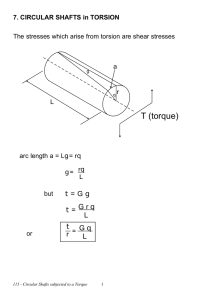
TORSION OF RECTANGULAR BARS TORSION OF RECTANGULAR BARS The analysis of circular shafts was based upon the assumption that plane cross sections remain plane and undistorted. If the cross section of the shaft is not circular, experiments showed that the cross section distort and do not remain plane. Therefore, the formulas for shear distribution and torsional rigidity derived for circular shafts can not be applied to noncircular members. Figure 3.10 shows the distortion of a rectangular bar caused by the torque T. The two significant features of the deformation are: • The cross sections become distorted. • The shear strain (and thus the shear stress) is zero at the edges of the bar and largest at the middle of the sides. For the rectangular bar in Fig. 3.12 that carries the torque T, results obtained by numerical methods determine that the maximum shear stress τ and the angle of twist θ are given by: