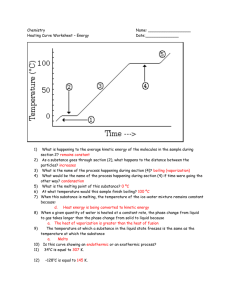
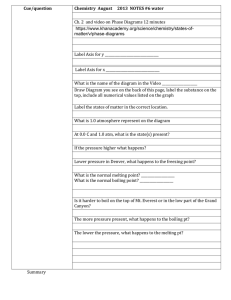
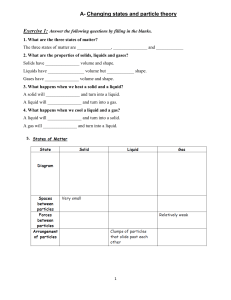
Stage 1 Chemistry Worksheet 1: Kinetic Theory of Matter Name: __________________ 1. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) Use your knowledge of the kinetic theory of matter to explain the following observations: Solids are difficult to compress Solids have a definite shape Liquids can be poured Gases are easily compressed Gases fill the container they are placed in Sidewalks are designed with cracks between the slabs. If someone is wearing perfume, the people closest smell it first, and only later do people farther away. Air needs to be added to a car's tires in the winter to keep them at the proper pressure. A balloon placed in the fridge contracts An aerosol can explodes when heated in a fire. Steam burns are more dangerous than water burns. When chopping onions, cold onions will cause less eye irritation than onions at room temperature. When people wearing glasses walk from an air conditioned room out into the humid Darwin weather, their glasses often fog up. It feel much hotter at 33C the wet season (high humidity) that 33C in the dry season (low humidity) 2. Thermometers rely on the expansion and contraction of liquids in a thin sealed glass tube from which the air has been removed. Two common liquids used are mercury and alcohol: Material Mercury Alcohol Melting Point -39 C -117 C Boiling Point 357 C 78 C a) Explain why liquids expand and contact at different temperatures. b) Explain why the air is removed from the tubes containing the liquid. c) Explain how mercury and alcohol thermometers are suitable for use in different conditions. 3. Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of high concentration to low concentration resulting in the even mixing of substances. a) Explain in which states of matter diffusion can occur. b) Explain in which state of matter diffusion will occurs the fastest. c) Explain factors that may affect the rate at which diffusion occurs d) Bromine gas particles are about twice as heavy and oxygen gas particles. Explain which gas you would expect to diffuse faster and what other factor this would depend on. 4. The following table shows the melting and boiling points of some different elements and compounds. Material Melting Point (C) Boiling Point (C) Aluminum 659 2,327 Ethyl alcohol -114 78.3 Lead 328 1,750 Mercury -38.8 357 Oxygen -219 -183 Water 0 100 Sulfur Dioxide -75 -10 a) b) c) d) State the materials that would be solids at 50C. State the materials that would be liquids at 70C State the materials that would be gases at 200C. Explain why different materials have different melting and boiling points. 5. a) b) c) d) e) Identify the change of state in the following examples: fat from a roasting dish becomes hard you can see steam as you heat up a pot of soup butter becomes very runny when left out on a hot day you breathe air onto your sunglasses and then give them a wipe. mothballs made of naphthalene disappear after being placed in the wardrobe. 6. Explain the difference between boiling and evaporation 7. Most solids when placed in liquids of the same material will sink. For example solid lead will sink in molten lead. However we all know ice floats in our drinks. a) Explain why we would expect solids to sink in liquids of the same material. b) Explain why ice floats in water. 8. The heating curve shown below is a plot of temperature vs time. It represents the heating of substance X at a constant rate of heat transfer. Answer the following questions using this heating curve: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) In what part of the curve would substance X have a definite shape and definite volume? In what part of the curve would substance X have a definite volume but no definite shape? In what part of the curve would substance X have no definite shape or volume? What part of the curve represents a mixed solid/liquid phase of substance X? What part of the curve represents a mixed liquid/vapor phase of substance X? What is the melting temperature of substance X? What is the boiling temperature of substance X? In what part(s) of the curve would increasing kinetic energy be displayed? In what part of the curve would the molecules of substance X be farthest apart? In what part of the curve would the molecules of X have the lowest kinetic energy? In what part of the curve would the molecules of X have the greatest kinetic energy? Explain why the temperature of the material does not change during sections II and IV. 9. The boiling point of water at sea level is approximately 100°C and it decreases by 1°C for every 300 m of altitude. a) If you were camping near the top of Mt Kosciuszko at 2100 m above sea level, at what temperature would water boil? b) Mt Everest is 8848 m high. At what temperature would water boil at the summit? c) Explain why mountain climbers use a pressure cooker to cook their food. 10. The following diagram shows the phase changes of carbon dioxide. a) Label the lines that represent the melting phase change and boiling phase change of carbon dioxide. b) Describe the effect of changing pressure on the boiling point of carbon dioxide. c) Compare the effect of changing pressure on the melting and boiling point of carbon dioxide. d) State the change of state that occurs for carbon dioxide at normal air pressure (1 atm) and the temperature at which it occurs. e) Describe the general conditions under which materials will sublime.