The nucleus and Radioactivity
What is the Strong force?
+ +
Without the strong force, protons in the nucleus would be impacted by the electromagnetic force and repel each other.
+
+
+
+
The strong force is one of four forces on Earth
(gravitational force, electromagnetic force, weak force and strong force). It gets rather complicated, but think of the strong force as the glue that holds an atomic nucleus together.
Since the strong force is a short-range force, and protons and neutrons are REALLY close together in a nucleus, the strong force holds neutrons and protons together.
TRIVIA: If the strong force is short-ranged, what is the electromagnetic force? How does it impact protons in the nucleus?
Strong Force vs. Electromagnetic Force
+
+
Help.
+
+
+
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
In an atom, the strong force becomes the super hero as long as the protons and neutrons are really close together. In other words, when there are only a few protons and neutrons, the strong force keeps the nucleus of an atom together.
When a nucleus increases its number of protons and neutrons, the electromagnetic force ends up taking over and the protons repel each other.
This leads to radioactive decay.
That’s why atoms with 83 or more protons end up being radioactive.
Radioactive Decay
When the strong force is not strong enough to hold a nucleus together tightly, it can begin to decay.
The process of nuclei decaying and sending out matter and energy is called Radioactivity.
Nuclear radiation is when a nucleus decays and sends out particles as well as energy.
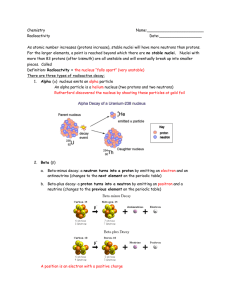
The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma radiation
.
Alpha Particle
+
+
When the strong force is unable to hold a nucleus together, an alpha particle is emitted.
An alpha particle is extremely massive when compared with Beta and gamma radiation (7,000 times more massive than a beta particle) .
Description: high-energy helium-4 nucleus
Symbol:
Mass:
Charge:
Because they have a high mass and energy, alpha particles interact with matter frequently. They can also travel through solids, liquids, and gases, but they’re the least penetrating form of nuclear radiation (a sheet of paper can stop them).
-‐
Description: high-energy helium-4 nucleus
Symbol:
Mass:
Charge:
The weak force, another of the four forces, can cause neutrons to decay into protons. When this decay happens, the nucleus emits an electron.
A beta particle is a high-energy electron that is given off when a neutron decays into a proton.
Beta particles are faster than alpha particles and much more penetrating. it takes a sheet of aluminum, about 3 mm thick to absorb most beta radiation.
Description: high-energy helium-4 nucleus
Symbol:
Mass:
Charge:
Gamma rays are extremely high-energy electromagnetic waves. In order to stop them, lead bricks or other heavy materials are needed.
Gamma rays are emitted during alpha and beta decay. Gamma rays have no mass and no charge and travel at the speed of light.
During gamma decay, a nucleus loses energy, but no particles.
TRIVIA: How does gamma radiation relate to a trip to the dentist?