Chemistry Name:________________________ Radioactivity
advertisement

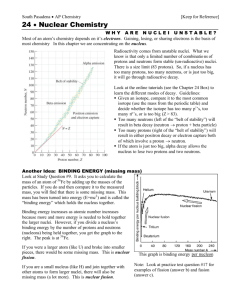
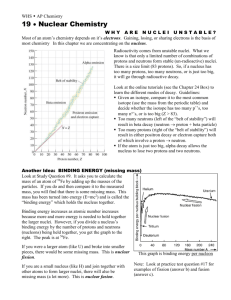
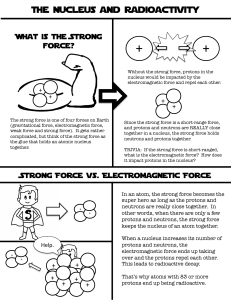
Chemistry Name:________________________ Radioactivity Date:__________________ As atomic number increases (protons increase), stable nuclei will have more neutrons than protons. For the larger elements, a point is reached beyond which there are no stable nuclei. Nuclei with more than 83 protons (after bismuth) are all unstable and will eventually break up into smaller pieces. Called Definition: Radioactvity = the nucleus “falls apart” (very unstable) There are three types of radioactive decay: 1. Alpha (α) nucleus emits an alpha particle An alpha particle is a helium nucleus (two protons and two neutrons) Rutherford discovered the nucleus by shooting these particles at gold foil 2. Beta (β) a. Beta-minus decay: a neutron turns into a proton by emitting an electron and an antineutrino (changes to the next element on the periodic table) b. Beta-plus decay: a proton turns into a neutron by emitting an positron and a neutrino (changes to the previous element on the periodic table) A position is an electron with a positive charge 3. Gamma (γ) = nucleus changes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state The EMR emitted is a gamma ray. Half-life: (t1/2) is the amount of time required for the amount of something to fall to half its initial value (radioactive half-life) 1. What is the half-life of the material in the graphic to the right? 2 days 2. Can you predict how much material will be left after 6 half-lives? 1.25 grams half-life 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 amt left 80 (orig amt) 40 20 10 5 2.5 1.25