Uploaded by
John Kim
Rules of Communication: Protocols, Encoding, and Message Formatting
advertisement

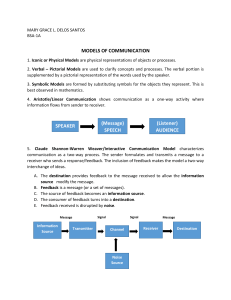
Chapter 3 – Rules of Communication - For communication to occur, devices must know “how” to communicate. Three elements of all communication methods - - Source or Sender o Message sources are people, or electronic devices that need to send a message to other individuals or devices. Destination or receiver o Receives the message and interprets it. Channel o Consists of media that provides the pathway over which the message travels from source to destination. Communication begins with a message or information, that must be sent from a source to a destination. - - Governed by rules called protocols Like a telephone call would not have a same protocol for using another medium, such as sending letter. Protocols must account for following requirements o An identified sender and receiver o Common language and grammar o Speed and timing of delivery o Confirmation or acknowledgement requirements Common protocols include: o Message encoding o Message formatting and encapsulation o Message size o Message timing o Message delivery options First Rule: - Encoding o Process of converting information into another, acceptable form for transmission. o Decoding reverses this process to interpret the information. Second Rule: - Message Formatting and Encapsulations o When a message is sent from source to destination, it must use a specific format or structure. o Letter writing is the most common forms of written human communication, and contains the following elements: An identifier of the recipient Salutation or greeting Message content Closing phrase Identifier of the sender Third Rule: - Communication Size