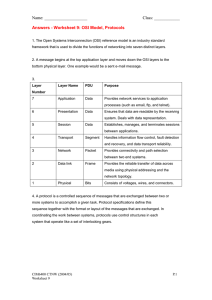
OSI MODEL OSI model is defined and is used to understand how data is transferred from one computer to another in a computer network In the most basic form two computers are connected to each other with LAN cables and connectors sharing data with help of network interface cards forms network. But if one computer is based on ms windows and the other one has mac OS installed , then how these computers are going to communicate with each other. In order to accomplish sucessful communication between computers or networks of different architectures, 7 layered OSI model was introduced by ISO IN 1984 containing 7 layers. Each layer is a package of protocols 1. Application layer :Application layer is used by network applications. Network application means computer application that use internet like Chrome, Firefox, Outlook,Skype,etc… Web browser is a network application in your PC, it does not reside in the application layer but it use its application layer protocols HTTP or HTTPS to do web browsing. There are dozens of application layer protocols that enable various functions at this layer. All these application layer protocols are collectively known as Application layer. These protocols form the basis for various network services like File transfer,web surfing,email,Virtual terminals,etc… File transfer ---- FTP web surfing ------ HTTP/S Email -------------- SMTP Virtual terminals --- TELNET Application layer provides services for network application by the help of protocols to perform user activities 2. Presentation layer ::It receives data from application layer.This data in the form of characters and numbers. This layer converts these characters and numbers machine understandable binary format.This function of presentation layer is called Translation. Before data is transmitted this layer reduces the number of bits that are used to represent original data. This bit reduction process is called Data compression.It also reduces the amount of OSI MODEL place used to stored the original file. As the file is reduced, it can be received at the destination in a very less time. To maintain integrity of data, before transmission data is encrypted. Encryption enhances the security of data. At sender side data is encrypted and at receiver side data is decrypted. Secure Sockets layer(SSL) protocol is used for encryption and decryption. 3. Session layer Session layer helps in setting up and managing connections,enabling sending and receiving of data followed by termination of connections or sessions. Session layer has its helpers called APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) which allows applications on different computers to communicate with each other. Just before a connection is establish to the server,server performs a function called Authentication. Authentication is a process of verifying who you are?. For this server uses its user name and password,once enterd user name and password are match a connection is established between your computer and server. After authenticating the user authorization is checked. Authorization is the process used by server to determine if you have permission to access a file. Authentication and authorization both performed by session layer Session layer keeps a track on the file being downloaded. It organizes as the data should come under the same data type (like image packet should come under image and text packet should come under text) This process is called Session management. 4. Transport layer::It controls the reliability of communication through segmentation, flow control, error control. a) Segmentation: The data received from session layer is divided into small data units called segments. Each segment contains a source and destination port number and a sequence number. OSI MODEL Port number helps to direct each segment to the correct application. Sequence number helps to reassemble the segment in correct order to form correct message at receiver. b) Flow control::Transport layer controls the amount of data being transmitted. Consider we connected mobile to the server, server can send data at speed of 100 MBps but phone can receive only at speed of 10 MBps. If the server giving data at 50 MBps , the phone by making use of transport layer sends a message to the server to slow down the speed to 10 MBps. c) Error control::If some data does not arrive the destination, transport layer uses its Automatic Repeat Request scheme to retransmit the lost or corrupted data. A group of bits called Checksum is added each segment by the transport layer to find out the received corrupted segment Transport layer protocols Transmission control protocol(TCP) – has feedback, slow User datagram protocol (UDP) -- no feedback, fast Transport layer perform services ::: 1. Connection- oriented transmission(uses TCP) 2. Connectionless transmission(uses UDP) 5. Network layer::It receives segments from transport layer. This layer works for the transmission of received segments from one computer to another located in different networks. Data units in the network layer are called packets. It is the layer where to decide OSI MODEL The function of network layer are Logical addressing, Routing, Path determination. a) Logical addressing ::- IP addressing done in network layer is called Logical addressing. Every computer in a network has a unique IP address. Network layer assigns sender and receiver IP address to each segment to form an IP packet. IP address are assigned to ensure that each data packet can reach the correct destination. b) Routing::- It is the method of moving data packet from source to destination and it is based on the logical address format IPv4 and IPv6. c) Path determination::- The process of choosing the best path for delivery of data packets from source to destination is called path determination. It uses protocols OSPF,BGP,IS-IS. 6. Data link layer::It receives data packets from network layer. Data packets contains IP addresses of sender and receiver. There are 2 kinds of addressing 1. Logical addressing 2. Physical addressing Logical addressing is done at network layer. Physical addressing is done in data link layer where mac address of sender and receiver are assigned to each data packet to form a frame. Data link layer used for 1. Access data 2. Controls how data is placed and received from the media(media access control and error detection) 7. Physical layer::Physical layer converts received data from data link layer into signals and transmit over local media. At the receiver physical layer receives signal convert into bits and pass into data link layer as frames and frames again decapsulated and passes to the higher layers. Finally data is moved to application layer . Application layer protocols makes the sender message visible in the receiver computer screen