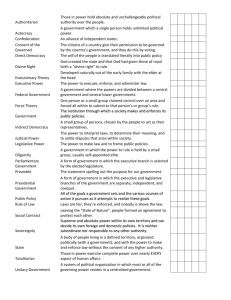
United States Government Module #0 - Introduction Key Questions 0.0 What Is Government? What is government? Government is the institution that allows a society to make and enforce public policies. What are the basic powers of government? The basic powers of government are: 1. the power to make laws (legislative power) 2. the power to execute laws (executive power) 3. the power to interpret laws (judicial power). What are the four defining characteristics of a state? The four defining characteristics of a state are: 1. a population, 2. living in a defined territory, 3. with a government 4. that can make and enforce law without the consent of any higher authority (sovereignty). What is the difference between the theories of divine right and social contract? Divine right: The government is made up of those chosen by God to rule a certain territory. The population must obey their ruler. Social contract: The people chose to give the state enough power to promote the well-being of everyone and that all political power comes from the will of the people. What is the purpose of government? The purpose of government is to: 1. provide justice, 2. ensure safety, and 3. promote the wellbeing of its citizens. 0.1 Types of Government How can governments be classified? Governments can be classified according to: 1. who can participate, 2. how power is shared geographically, and 3. how legislative and executive powers are separated. Which governments are classified by who can participate? Democracies and dictatorships are classified according to who can participate in government. Which governments are classified by how power is shared geographically? Unitary, federal, and confederation-style governments are classified based on how power is divided geographically. Which governments are classified by how legislative and executive powers are separated? Presidential and parliamentary governments are defined by the relationship between the executive and legislative branches. What is the difference between autocracy and oligarchy? In an autocracy, one person holds total political power, while in an oligarchy a small elite group shares political power. Both are forms of dictatorships, holding absolute and unchallenged authority over the people, who have no say in government. What is the difference between direct and indirect democracy? In a direct or pure democracy, the people pass laws by discussing and voting on them in meetings, such as town meetings. This system works only in small communities. In an indirect or representative democracy, the people elect agents who make and carry out the laws. These representatives rule with the consent of the governed and can be removed by the people at election time. 0.2 Fundamentals of Democracy What are the basic concepts of democracy? The basic concepts of democracy are: 1. Recognition of the fundamental worth and dignity of every person 2. Respect for the equality of all persons 3. Faith in majority rule and an insistence upon minority rights 4. Acceptance of the necessity of compromise 5. Insistence upon the widest possible degree of individual freedom To what are citizens entitled under the democratic concept of equality? All citizens are entitled to equality of opportunity and equality before the law. This means that no person should be held back based on gender, race, color, or religion. What is the difference between the duties and responsibilities of citizens? Every citizen has duties that they must obey. Every citizen also has responsibilities they should fulfill to improve the quality of their government and community. What are some of the duties of a citizen? Duties of a citizen include: 1. Serving on a jury 2. Serving as a witness 3. Attending school 4. Paying taxes 5. Obeying local, state, and national laws 6. Draft registration 7. Respecting the rights of others What are some of the responsibilities of a citizen? Responsibilities of a citizen include: 1. Voting 2. Volunteering 3. Participating in civic life 4. Understanding the workings of our government What effect does demand have on prices? Greater demand tends to increase prices, while lower demand tends to decrease them. United States Government Module #0 - Introduction Word Bank 0.0 What Is Government? 1. Divine right theory: the theory that governments gain their authority from the will of God 2. Executive power: the power to enforce and administer laws 3. Government: the institution that allows a society to make and enforce public policies 4. Judicial power: the power to interpret laws 5. Legislative power: the power to make laws 6. Population: a body of people 7. Public policies: all the things a government decides to do 8. Social contract theory: the theory that the people can withhold power from an unjust government 9. Sovereignty: the absolute power within its own territory to decide domestic and foreign policies 10. State: a body of people, living in a defined territory, with a government that can make and enforce law without the consent of any higher authority. 11. Territory: land with known and recognized boundaries. 0.1 Types of Government 12. Autocracy: government in which a single person holds all political power 13. Confederation: an alliance of independent states 14. Democracy: a government in which supreme authority rests with the people 15. Dictatorship: a government in which all power rests with an individual or small group 16. Direct democracy: the people pass laws by discussing and voting on them in meetings, such as town meetings; also known as pure democracy 17. Division of powers: the split of power between central and local governments 18. Federal government: a government in which power is divided between one central and several local governments 19. Indirect democracy: the people elect agents who make and carry out the laws; also known as representative democracy 20. Oligarchy: government in which a small, usually self-appointed group has the sole power to rule 21. Parliamentary government: a government in which the executive branch is part of the legislative branch and subject to its control 22. Presidential government: a government with separate executive and legislative branches 23. Unitary government: a government in which all power belongs to one central agency 0.2 Fundamentals of Democracy 24. majority rule: the principle that the will of the majority controls the actions of government 25. compromise: the process of blending and adjusting competing views and interests 26. citizen: one who holds certain rights and responsibilities within a state 27. free enterprise system: an economic system characterized by the private ownership of capital goods, private investment, and a competitive marketplace that determines success or failure