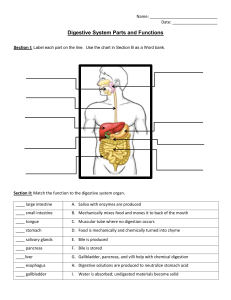
Digestion Lab Part A: Digestion in the Mouth All food enters the digestive system through the mouth. Food is chewed to begin breaking it down and carbohydrates (sugars) are initially broken down by the enzyme amylase. Starch is a long chain (polymer) of glucose molecules found in foods such as the gum used in this lab. Iodine is used as a starch indicator because the chemical reaction between the two causes a color change. A person was given a piece of Double Bubble Gum. They cut it in half and placed one half in a petri dish and began chewing the other half. The non-chewed piece was flatted out and iodine was placed on it for 5 minutes. The original color of iodine was a brownish/yellowish and after 5 minutes the student noticed that it turned a bluish/blackish. 1. What chemical change occurred and why? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ After 20 minutes of chewing the Double Bubble, the student flatted out the chewed gum and added 5 drops of iodine to the chewed gum sample in the Petri dish. Again the original color of the iodine was a brownish/yellowish and after 20 minutes the student noticed that it remained the same, brownish/yellowish. 2. Was the reaction between the gum and iodine the same as in the previous experiment? Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What enzyme is digesting the starch into glucose and caused this change in taste and reaction with iodine? __________________________________ 4. One starch is breaking down into many glucose molecules. A large molecule made of many small molecules is called a _______________________________. The small molecules are known as _________________________________. 5. What is the difference between chemical and mechanical digestion? Look in your Biology book page 979 Figure 32.11. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Part B: Length of your Digestive System A student measured and constructed a representation of the length of their digestive tracts using yarn pieces. Data Table 1: Organ Length (inches) Mouth 5.5 Esophagus 13 Stomach 7 Small intestine 296 Large intestine 74 Total Digestive System Length 395.5 Create a Bar Graph to compare the tract lengths of lab group to lab group. Don’t forget to label your x-axis and y-axis and title your graph (make it a winning graph)! Analysis: 1. Are all organs of the digestive system the same length? _________________________________________ 2. What is the longest organ in your digestive system? _____________________________________________ 3. How does the length of the small intestine relate to its function? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Why are the names “small intestine” and “large intestine” misleading? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Accessory organs such as the liver, gallbladder and pancreas produce enzymes which help to breakdown food during digestion. Why are they not included in the list of organs food travels through? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Which macromolecule is initially broken down in your stomach? ____________________________________ 7. Why don’t all humans have the same length digestive system? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Use page 978 from the Biology book, to fill in the chart. Enzyme Digestive Organ Function