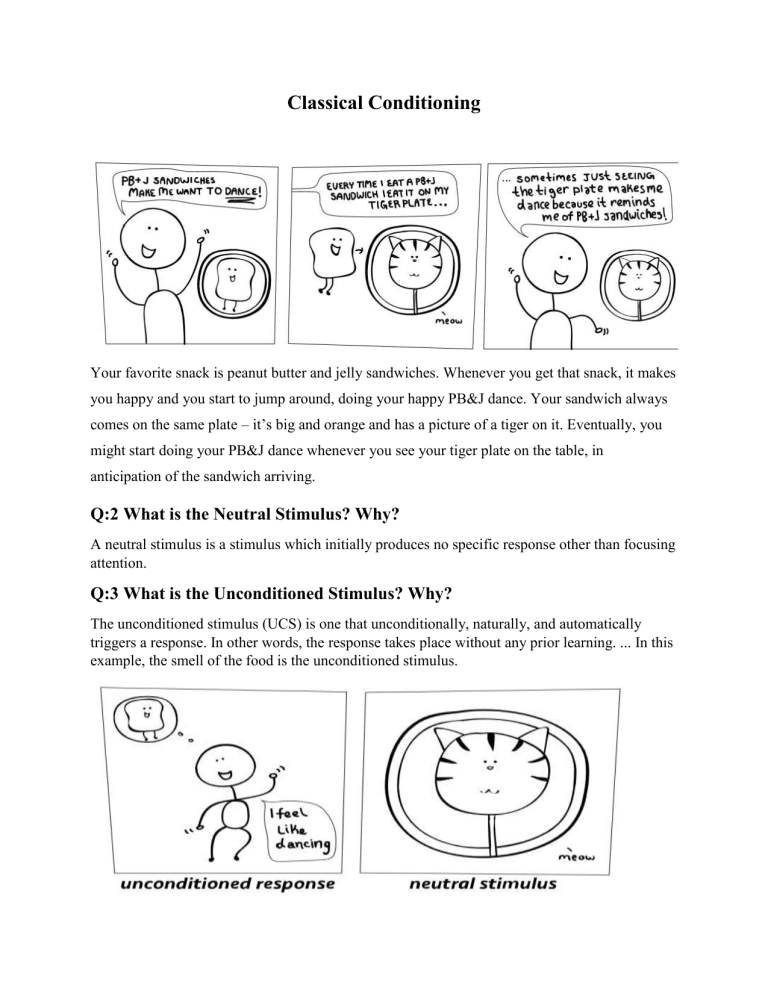
Classical Conditioning Your favorite snack is peanut butter and jelly sandwiches. Whenever you get that snack, it makes you happy and you start to jump around, doing your happy PB&J dance. Your sandwich always comes on the same plate – it’s big and orange and has a picture of a tiger on it. Eventually, you might start doing your PB&J dance whenever you see your tiger plate on the table, in anticipation of the sandwich arriving. Q:2 What is the Neutral Stimulus? Why? A neutral stimulus is a stimulus which initially produces no specific response other than focusing attention. Q:3 What is the Unconditioned Stimulus? Why? The unconditioned stimulus (UCS) is one that unconditionally, naturally, and automatically triggers a response. In other words, the response takes place without any prior learning. ... In this example, the smell of the food is the unconditioned stimulus. Q:4 What is the Unconditioned Response? Why? In classical conditioning, an unconditioned response is an unlearned response that occurs naturally in reaction to the unconditioned stimulus. For example, if the smell of food is the unconditioned stimulus, the feeling of hunger in response to the smell of food is the unconditioned response. Q:5 What is the Conditioned Stimulus? Why? A conditioned stimulus is a substitute stimulus that triggers the same response in an organism as an unconditioned stimulus. ... After repeated exposure, the neutral stimulus becomes paired with the unconditioned response and becomes a conditioned stimulus. Q:6 What is the Conditioned Response? Why? A conditioned response is a behavior that does not come naturally, but must be learned by the individual by pairing a neutral stimulus with a potent stimulus. The potent stimulus is one that does not require any learning or conditioning to respond to appropriately. Q:7 How might we unconditioned (extinguish) the association created in the ad? OPERANT CONDITIONING When a lab rat presses a blue button, he receives a food pellet as a reward, but when he presses the red button he receives a mild electric shock. As a result, he learns to press the blue button but avoid the red button. Q:2 What type of consequence (positive or negative, reward or punishment) is given in the ad? Explain your choice.