Chapter 2. Force Systems
FORCE
• A
Force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object’s interaction with another object.
Whenever there is an interaction between two objects, there is a force upon each of the objects. When the interaction ceases, the two objects no longer experience the force. Force only exist as a result of an interaction.
(www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/Lesson-2/The-Meaning-of-
Force.html)
Force Classification.
Contact force : Concentrated / Distributed
Body force: generated by virtue of being in a force field.
Weight : force of gravitational attraction,
Action / Reaction: from Newton’s Third law, the action of a force is always accompanied by an equal and opposite reaction.
It is essential to distinguish between the action and the reaction in a pair of forces.
Concurrent Force: Two or more forces are said to be concurrent at a point if their lines of action intersect at that point.
Representation of a Force .
Must specify:
• Magnitude
• Direction
• Point of application
Principle of Transmissibility .
A force may be applied at any point on its given line of action with out altering the resultant effects of the forces external to the rigid body on which it acts.
(a) Forces acting at point A, Using parallelogram of forces, resultant R through point A.
(b) Concurrent force at A. Line of action intersecting at A. Using parallelogram of forces, resultant R through point A.
(c) Using triangle of forces, resultant R through point A
(d) Line of action not through point A.
This type of combination to be avoided.
Rectangular components
F = F x
+ F y
F = F x
i+ F y j
Resolution of a vector
R = F
1
+ F
2
= ( F
1x i + F
1y j) + ( F
2x i + F
2y j) or
R x i + R y j = (F
1x
+F
2x
) i + (F
1y
+ F
2y
) j
R x
= F
1x
+F
2x
= Σ F x
R y
= F
1y
+ F
2y
= Σ F y
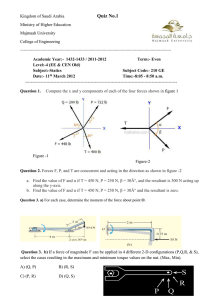
Sample Problem 2/1
Given : three forces specified in three different ways.
Required : the x and y scalar components of each of the three forces
Assumptions : none
Discussion point : what are the three different ways used to specify the forces?
1.->
2.->
3.->
Sample prob. 2/1, solution
Sample Problem 2/2
Given : two forces P and T acting on structure B
Required : single equivalent force
R , acting on B
Assumptions : none
Discussion:
1) What is the principle that must be used to combine the forces?
2) What are the techniques that could be employed?