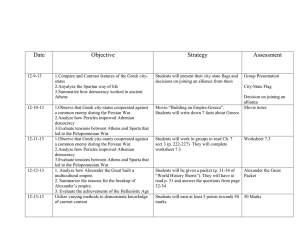
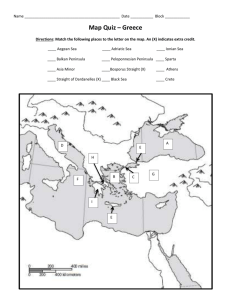
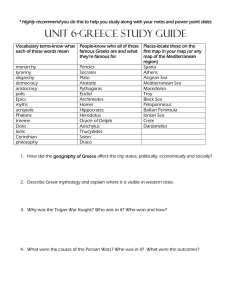
Athens and Sparta Worksheet Ancient Greece wasn't one large empire but a collection of smaller city-states. The term the Greeks used was polis, which means “city-state”. A polis was bigger than a city but smaller than a state. They were scattered throughout the Mediterranean area. Some were sea-ports while others were more inland. The two most famous city-states were Athens and Sparta. Although the people living in these city-states were all Greek, each city-state did different things and had different beliefs. Let’s examine these differences by looking at two city-states. Athens- was the most famous of all the city-states of ancient Greece. Athens was located on Attica, allowing them to rely on fishing and trading to drive their economy. It was the birthplace of democracy and home to great philosophers like Plato and Socrates. It was also home to historians, scientists, mathematicians, and other great thinkers. Athenian society was divided into three classes: Freemen including all male citizens, Metics who were outsiders who were not allowed to own land, and Slaves who could be bought and sold as property. Athens was famous for its giant fleet or ships (navy), which they used to help defeat the Persians. Athenians were polytheistic and believed in a common Greek mythology that included the pantheon of gods such as Zeus. A great rivalry with another city-state, Sparta led to the Peloponnesian War. This war eventually ended in a victory for Sparta. Sparta- had the strongest military of all ancient Greek citystates. Located inland on the Peloponnesian Peninsula, instead of fishing and trading, the focus of this city-state was constantly on war. They developed a military economy. Boys were expected to be trained as soldiers, while girls were expected to grow up and bear children who grew up to be soldiers. To make sure that the army got as many Spartan soldiers as it needed, Sparta depended on slaves (called Helots) from nearby settlement to do their manual labor. Spartan society was divided into three classes: citizens who were males of the ruling class, Helots who had been enslaved, and free people from neighboring provinces under Sparta’s control. When the Greeks were at war with Persia, many people turned to the Spartans to ensure their protection. Sparta’s government was an Oligarchy, where a few powerful people made the decisions. Like all Greeks, Spartans were polytheistic and believed in a similar mythology as Athenians. 1. What were two important Greek city-states? a) _____________________, b) _____________________ 2. What was the Greek word for city-state? ____________________ 3. Athens was the birthplace of this important idea… ______________________ 4. Who were two famous philosophers from Athens? a) __________________, b) __________________ 5. Who won the Peloponnesian War? _____________________ 6. What were the Spartans famous for? ___________________________________________ 7. What were boys in Sparta expected to be when they grew up? ______________________________ 8. Who did the Spartans depend on to complete their manual labor? _____________________