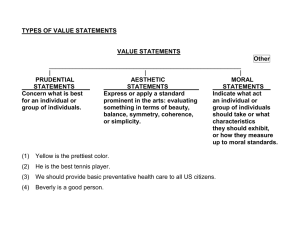
BUSINESS LAW CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS ETHICS /CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY-a process with the aim to embrace responsibility for the company's actions and encourage a positive impact through its activities on the environment, consumers, employees, communities, stakeholders and all other members of the public sphere who may also be considered stakeholders CATEGORICAL IMPERATIVE- an unconditional moral obligation that is binding in all circumstances and is not dependent on a person's inclination or purpose Utilitarianism- an ethical philosophy in which the happiness of the greatest number of people in the society is considered the greatest good; an action is morally right if its consequences lead to happiness, and wrong if it ends in unhappiness Moral Relativism- the view that moral judgements are true or false only relative to some particular standpoint and that no standpoint in uniquely privileged over all others Kantian Ethics-refers to a deontological ethical theory ascribed to the philosopher Immanuel Kant; focused on the rightness or wrongness of actions in and of themselves, rather than on the consequences of those actions Corporate Philanthropy-the act of a corporation or business promoting the welfare of others, generally via charitable donations of funds or time given to nonprofit organizations Torts-a wrongful act or infringement of a right leading to civil legal liability Greening-refers to a business that is functioning in the capacity where no negative impact is made on the local or global environment, the community, or the economy Corporate Governance-the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled; essentially involves balancing the interest of the many stakeholders in a company Diversity-a mixed workforce that provides a wide range of abilities, experiences, knowledge, and strengths Social Report- a report that entails businesses with a relationship to the society which they operate in