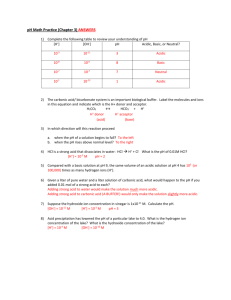
Name _______________________________ Period ______ Acids and Bases Worksheet 1. Identify the following as properties of acids, bases, or both. a. bitter ___base____________________ b. sour ____acid____________________ c. may conduct electricity __both______ d. slippery ___base_________________ e. reacts with metals while producing hydrogen gas ___acid_____________ f. neutralized by an acid to produce salt and water ___base________________ g. turns pH paper red ___acid_________ h. turns pH paper blue ___base________ 2. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution is measured to be 1.0 x 10-4 M. a. What is the hydroxide ion concentration? 1.0 x 10-10 M b. What is the pH of the solution? 4.0 c. Is the solution acidic or basic? acidic 3. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution is measured to be 1.0 x 10-9 M. a. What is the hydroxide ion concentration? 1.0 x 10-5 M b. What is the pH of the solution? 9 c. Is the solution acidic or basic? basic 4. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution is measured to be 3.2 x 10-11 M. a. What is the hydroxide ion concentration? 3.1 x 10-4 M b. What is the pH of the solution? 10.49 c. Is the solution acidic or basic? basic 5. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution is measured to be 0.016 M. a. What is the hydroxide ion concentration? 6.3 x 10-13 b. What is the pH of the solution? 1.80 c. Is the solution acidic or basic? acidic 6. Label these solutions as acidic, neutral, basic. a. pH = 2.6 ___acidic________________ b. pH = 7.0 ___neutral_______________ c. pH = 10.5 __basic________________ d. [H+] = 3.2 x 10-2 M ___acidic________ e. [H+] = 1.0 x 10-7 M ___neutral_______ f. [OH-] = 5.7 x 10-5 M __basic________ g. [OH-] = 2.2 x 10-10 M _acidic________ 7. What is the definition of an acid? An acid is a hydrogen ion donor. 8. What is the definition of a base? A base is a hydrogen ion acceptor, or a hydroxide ion donor. 9. Circle the acidic hydrogen or hydrogens in the following acids. Example: HCl a. HBr b. HNO3 c. H2SO4 d. CH3CO2H e. HCO2H f. H2CO3 g. H2NCH2CO2H 14. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration from the following pH values. Identify the solution as acidic, neutral or basic. 10. Circle the atom which is the hydrogen ion acceptor in the following bases. a. NaOH a. A N B pH = 7.0 ___1.0 x 10-7_______ b. KOH b. A N B pH = 2.7 ___2.0 x 10-3_______ c. Mg(OH)2 c. A N B pH = 13.0 __1.0 x 10-13______ d. NH3 e. CH3NH2 15. Write equations showing how each substance produces either H+ or OH–. Label the substance as an acid or a base. Example: A B HCO2H → H+ + HCO2– a. A B HCl → H+ + Cl– b. A B HNO3 → H+ + NO3– c. A B H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42– d. A B H2CO3 → 2H+ + CO32– e. A B KOH → K+ + OH– f. A B Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2OH– g. A B NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH– h. A B HCO2H → H+ + HCO2– i. A B CH3CO2H → H+ + CH3CO2– j. A B CH3NH2 + H2O → CH3NH3+ + OH– f. H2NCH2CO2H 11. Which reaction is equivalent to: HIO3 + H2O → H3O+ + IO3– a. HIO3 → H+ + IO3– b. HIO3 + H2O → H+ + IO3– c. HIO3 → H3O+ + IO3– d. HIO3 + H3O+ → H2O + IO3– 12. Write the chemical reaction which shows how ammonia produces hydroxide ion. NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH– 13. Calculate the pH of the following solutions and label the solutions as acidic, neutral or basic by circling the letter A, N or B. a. A N B [H+] = 1.0 x 10-2 M ___2.00___ + 16. Complete the following reactions. Make sure the equations are balanced. Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O -7 b. A N B [H ] = 1.0 x 10 M ___7.00___ a. H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 → MgSO4 + 2H2O c. A N B [H+] = 1.0 x 10-9 M ___9.00___ d. A N B [H+] = 2.7 x 10-5 M ___4.57___ b. CH3CO2H + NaOH → CH3CO2Na + H2O e. A N B [H+] = 7.0 x 10-7 M ___6.15___ f. A N B [H+] = 1.0 M ________0.00___ c. HCl + NaHCO3 → NaCl + H2CO3 + g. A N B [H ] = 0.15 M _______0.82___ d. CH3NH2 + HCl → CH3NH3Cl h. A N B [OH-] = 5.7 x 10-5 M __9.76__ i. A N B [OH-] = 2.2 x 10-10 M _4.34___ e. H2NCH2CO2H + HCl → H3NCH2CO2HCl j. A N B [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7 M __7.00__ k. A N B [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14 M _0.00___ f. H2NCH2CO2H + NaOH → H2NCH2CO2Na + H2O l. A N B [OH-] = 1.0 M ______14.00___ m. A N B [OH-] = 0.050 M ____12.70___ 2