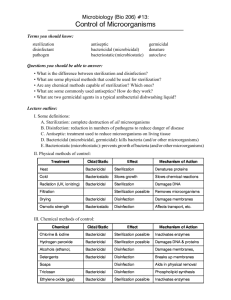
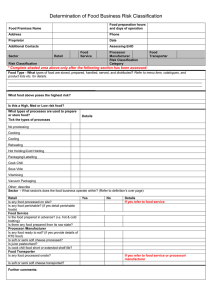
Spelling Words: Test 1: 1. Disinfection 2. Germicide 3. Exposure 4. Precaution 5. Hepatitis 6. Dehiscence 7. Traumatic 8. Preservative 9. Coagulate 10.Cautery 11.Electrode 12.Forceps 13.Keratosis 14.Cryosurgery 15.Abscesses Test 2: 1. Sanitation 2. Autoclave 3. Hemostat 4. Serration 5. Ratchet 6. Disease 7. Bactericidal 8. Resistance 9. Virulent 10.Spores 11.Aerobes 12.Anaerobes 13.Vector 14.Viable 15.Sterilization Terminology: 1. Sanitation: The process of making something sanitary. 2. Autoclave: An apparatus for sterilization by steam under pressure consisting of a strong closed boiler in which are placed a small quantity of water and a wire basket holding the articles to be sterilized. 3. Hemostat: an instrument, such as a clamp, that stop a hemorrhage by compressing a bleeding vessel. 4. Serration: The state of being serrated or notched. 5. Ratchet: a steplocking device on surgical instruments. 6. Disease: definite pathologic process having a distinctive set of symptoms and course of progression. 7. Bactericidal: substance that kills or destroys bacteria. 8. Resistance: body’s immune response to prevent infections by invading pathogenic microorganisms. 9. Virulent: highly pathogenic and disease producing; describes a microorganism. 10.Spores: bacterial life form that resists destruction by heat, drying, or chemicals. Spore-producing bacteria include botulism and tetanus. 11.Aerobes: microorganism that requires oxygen to live and reproduce. 12.Anaerobes: bacteria that require the absence of oxygen for growth and reproduction. 13.Vector: (biologic) a living, nonhuman carrier of disease, usually an arthropod; (mechanical) a carrier of disease that does not support growth. 14.Viable: capable of growing and living. 15.Sterilization: process, act, or technique for destroying microorganisms using heat, water, chemicals, or gases. 16.Disinfection: killing or rendering inert most but not all pathogenic microorganisms. 17.Germicide: chemical that kills most pathogenic microorganisms; disinfectant. 18.Exposure: the condition of being subjected to something, as to infectious agents or extremes of weather or radiation, which may have a harmful effect. 19.Precaution: A protective measure taken in advance. 20.Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver, due usually to viral infection but sometimes to toxic agents. 21.Dehiscence: separation or opening of the edges of a wound 22.Traumatic: causing or relating to tissue damage. 23.Preservative: substance that delays decomposition. 24.Coagulate: change from a liquid to a solid or semisolid mass. 25.Cautery: means, device, or agent that destroys or coagulates tissue. 26.Electrode: medium for conducting or detecting electrical current 27.Forceps: a two-bladed instrument with a handle, used for compressing or grasping tissues in surgical operations, handling sterile dressings, and other purposes. 28.Keratosis: premalignant overgrowth or thickening of the upper layer of epithelium or horny layer of the skin 29.Cryosurgery: the surgical destruction of tissue using freezing temperature with liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide 30.Abscesses: an enclosed collection of liquefied tissue, known as pus, somewhere in the body.