ESL - 1 Organisms
advertisement

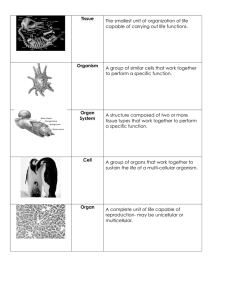
Definition Example Questions: 1. What are some functions of a cell? a. ______________________________ b. ______________________________ c. ______________________________ Organism 2. List an example of a unicellular organism? a. ______________________________ 3. List four examples of multicellular organism? a. ______________________________ b. ______________________________ Write a sentence Draw a picture Definition Example c. ______________________________ d. ______________________________ 4. Are humans multicellular or unicellular? (circle one) 5. What characteristic distinguishes a unicellular organism from a multicellular organism? Cell Write a sentence Draw a picture Definition Example Video (2.54 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFuEo2ccTPA Read: Introduction to Cells Unicellular Write a sentence Draw a picture Definition Example Multicellular Write a sentence Draw a picture All living organisms (living thing) are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life where all life’s functions occur. Unicellular organisms (single-celled organism) like bacteria are composed of just one cell, whereas multicellular organisms (many-celled organism) can be composed of trillions of cells. Humans are composed of 100 trillion cells (100,000,000,000,000). Examples of multicellular organisms include protists, fungi, plants and animals. Most plant and animal cells are microscopic and therefore can only be observed under the microscope. The one cell of a unicellular organism must be able to perform all the functions necessary for life. These functions include metabolism, homeostasis and reproduction. Specifically, these single cells must transport materials, obtain and use energy, dispose of wastes, and continuously respond to their environment. The cells of a multicellular organism also perform these functions, but they may do so in collaboration with other cells. But a cell, even the single cell of a unicellular organism, must be able to interact with its external environment. The cell must be able to bring molecules in from the outside, and expel unwanted waste products. Knowing the structure and functions of organelles (little organs) of the cells like the ribosomes, nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts are necessary to understand how a cell functions, and ultimately you.