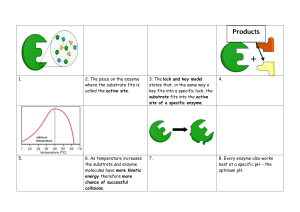
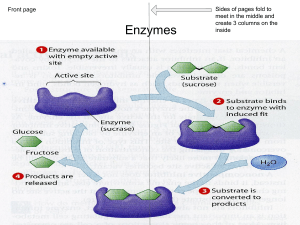
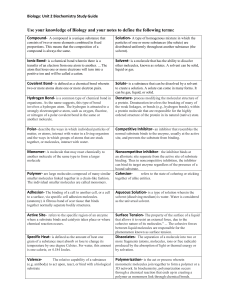
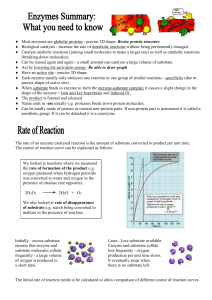
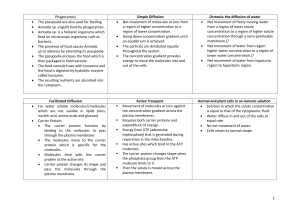
Glucose Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis Enzyme Substrate Denature Lipid Protein Starch Organic Inorganic Acid pH Neutral Basic pH Homeostasis Active Site Lock and Key Model Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Monosaccharide Building a larger molecule Breaking down- smaller molecules Protein that speeds up the rate of chemical reactions Substance acted upon by an enzyme Breakdown of an enzyme Fat molecule(glycerol +3 fatty acids) Amino acids -building block Long chain of glucose Carbon and Hydrogen pH 7 pH less than 7 pH more than 7 water(H2O) Internal stability Area on enzyme where substrate attaches Substrate fits exactly into the active site of an enzyme Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration Molecules move from low to high using energy Diffusion of water