Review PPT for Sensation & Perception
advertisement
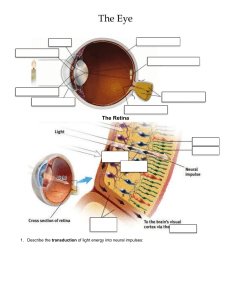
• Name the 7 senses. • • • • • • • Taste (gustation) Touch (tactile) Smell (Olfaction) Vision Hearing (audition) Balance (vestibular) Kinesthesis (movement) • • • • • What parts of the eye is responsible for each of the following: Protects the eye from dust, etc. Allows light into the eye Adjusts (dialates/constricts) the amount of light Focuses the incoming light onto the retina • • • • Cornea Pupil Iris Lens • What is your retina’s center focus point and what receptors that pick up colors and details are clustered around it? • Fovea • Cones • What receptors in your retina detect black, white, & gray and are best in dim light (also peripheral vision)? • Rods • What is the transforming of stimulus energies (like sights, sounds, smells) into neural impulses our brains can interpret called? • Transduction • Your retina sends messages to the brain through what? • What part of the brain must it pass through before being processed? • Optic Nerve • Thalamus • In what area of your brain is vision processed (2 parts)? • Occipital Lobes • Visual Cortex • What is the place where your optic nerves cross to deliver information to the opposite hemisphere? • Optic Chiasma • What nerve cells pick up motion, shapes, lines, etc…? • Feature Detectors • What theory of color argues that there are 3 color receptors and the combinations of them make millions of colors? • Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Color Theory • Make sure you also know the Opponent Process Theory & after images • What type of deafness occurs with damage to the middle or outer ear (eardrum, ossicles…)? • Conduction Hearing Loss • What type of deafness is due to damage to hair cells or nerves of the inner ear? • Sensorineural • Can be caused by disease, loud noises… • Cochlear Implants • What theory argues that pain is felt when small nerve fibers in the spinal cord are stimulated? • Gate Control Theory of Pain • What are the 5 taste sensations? • • • • • Sweet Sour Salty Bitter Umami • Our senses working together to interpret the world around us is called? • Sensory Interaction • Where is our equilibrium that controls our sense of balance located? • Inner Ears • What sense produces the strongest emotional reaction and why? • Smell-direct link to the brain near the limbic system (no thalamus) • What are the 2 types of perceptual processing? • Which one is due to our prior knowledge and schemas & our brain fills in the gaps? • Top Down-our brain tells us what it is then we look at details • Bottom Up-looking at details to put the “puzzle pieces” together • Our ability to focus our attention on a single talker while conversations and noise exist in the background is called… • Cocktail Party Phenomenon • Our conscious focus of awareness on stimuli is called…(we can only focus on one thing at a time) • Selective Attention • Mr. Boschman leaves the room and Mr. Abdullah comes in to fill in for him. You do not notice that you have a different teacher because you are so focused on the lab. What is this called? • Change Blindness • Remember Vegas? • You are driving and hit a man on a bike because you didn’t notice he was crossing the crosswalk. What is this an example of? • Inattentional Blindness • Remember the Penguin & Gorilla? • The minimum amount of light, sound, pressure, taste, or smell you need to detect it 50% of the time is called… • Absolute threshold • The smallest amount of change in a stimulus needed before we actually detect a change is called… • Just Noticeable Difference (JND) • What rule says the greater the intensity of the stimulus the greater the change is needed to be noticed? • Ex: if you are listening to your tv at 90, you will need to turn it down by a lot more than if the volume were at 20. • Weber’s Law • Just remember Thalia handling all the $$$ • If you were to see an object and understand it based on seeing the object against its background, you would be performing what process? • Figure-Ground Relationship • What branch of psychology argues that we look at the WHOLE picture (grouping) instead of focusing on parts? • Gestalt Psychology What part of Gestalt Psychology is each of the following: • We group objects that are close together as being part of same group • We see objects as similar in appearance as being part of same group • Proximity & Similarity • Eleanor Gibson’s Visual Cliff experiments suggested that infants were capable of detecting what? • Depth perception • The difference in our vision between eyes is known as…(differences are greater as object gets closer to your eye) • You need both eyes to see what kinds of cues? • Retinal Disparity • Binocular Cues • What type of monocular cues are described in the following: • Parallel lines seem to meet in the distance • The smaller the object the farther away we think it is • If one object partially blocks another we think it’s closer • Linear Perspective • Relative Size • Interposition • What is the illusion that if 2 or more lights are blinking on and off we think it is bouncing back and forth? • Phi Phenomenon • We have the tendency to perceive things in a certain way. For example, Jacob believes in UFOs. He sees something in the sky and automatically thinks it is a UFO (even though it might be something else. What is this an example of? • Perceptual Set