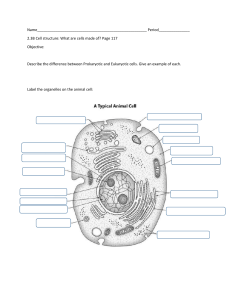
Advanced Bio Cell Study Guide Note: The test is not necessarily limited to these items. Cell Theory What are the 3 components of the cell theory? Who coined the term “cell”? What was he looking at? Why did he call them cells? Which scientist discovered bacteria? What did he call them? Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells What 4 things do all cells have in common? Be able to identify these cell shapes: coccus, bacillus, and spirillum. What is the DNA like in bacteria? Is it in a nucleus? What do the words “prokaryote” and “eukaryote” mean? What structures are different and the same between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Make a Venn diagram below. What structures are different and the same between plant and animal cells? Make a Venn diagram below. Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Know the functions of all of the organelles mentioned/studied in class and what the organelles look like. Study your cell booklet. o Nucleus o Nucleolus o Cytoplasm o Cell Membrane o Cell Wall o Centrosome o Mitochondria o Chloroplast o Lysosome o Golgi o Rough ER o Smooth ER o Ribosomes Cell Membrane Structure What is the cell membrane made of? How many layers make up the cell membrane? What are the channels through the membrane made of? Cell Membrane Transport What is diffusion? What is a concentration gradient? In which direction does it always flow? In passive transport, molecules move from an area of _______ concentration to an area of _______ concentration. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? What is active transport? What is endocytosis? What is exocytosis? What does hypertonic mean? What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution? What does hypotonic mean? What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution? What does isotonic mean? What happens to a cell in an isotonic solution?