IONS TABLE
advertisement

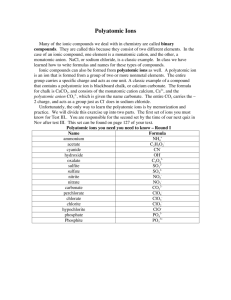
Ions Table Cations: Monatomic: Positive ions Contains one element Anion: Polyatomic: Negative ion Contains more than one element The charge on a monatomic ion can be worked out by looking at its position in the periodic table e.g. Oxygen is in group six of the periodic table so has six outer electrons. Oxygen gains two electrons to complete its outer shell so the ion of oxygen is O2- and is known as the oxide ion. Sodium is in group one of the periodic table so has one outer electron. Sodium loses one electron to obtain a full outer shell so the ion of sodium is Na+ and is known as the sodium ion. Polyatomic ions need to be learnt. At the very least learn the shaded polyatomic ions in the table below, Monatomic Cations Polyatomic Anions Silver Ag+ Hydroxide OH- Copper (II) Cu2+ Nitrate NO3- Iron (II) Fe2+ Carbonate CO32- Iron (III) Fe3+ Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3- Zinc Zn2+ Sulfate SO42- Lead Pb2+ Manganate (VII) MnO4- Polyatomic Cations Ammonium NH4+ [Sulphate (VI)] Chlorate (I) ClODichromate (VI) Cr2O72Sulfite SO32- D:\731462468.doc [Nitrate (V)] [Sulphate (IV)]