ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE
advertisement

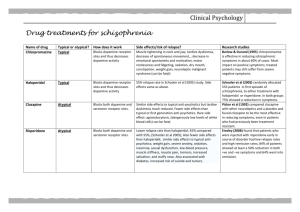
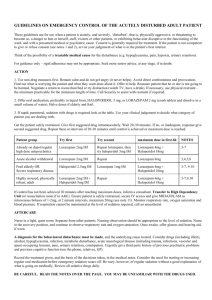
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Intravenous Haloperidol (Haldol®) Major Indications Rapid neuroleptization in patients exhibiting acute psychotic behavior Mechanism of Action Precise mechanism of action is unclear. Haloperidol appears to depress the central nervous system at the subcortical level of the brain by inhibiting the reticular activating system as well as antagonizing the CNS catecholamine (dopamine) receptors. Pharmacokinetics IV IM Onset of Effect 5-10 minutes 20-30 minutes Peak Effect 20-30 minutes 50-60 minutes Duration of Effect 4-5 hours 4-6 hours Monitoring Blood Pressure Mental Status Dosing and Administration* IM / IV Push (over 1 minute) / IVPB Mild Agitation: Moderate Agitation: Severe Agitation: 0.5-2 mg 2-5 mg 10-20 mg May repeat bolus doses every 20-60 minutes until calm achieved, then administer 50% of the maximum bolus dose required for good effect every 6 hours. Doses up to 1200 mg in the 1st 24 hour period have been reported in the literature. Continuous infusions, 100 mg haloperidol in 100 ml D5W, have been used in doses of 1-40 mg/hr *IV administration is not FDA-approved, however, haloperidol lactate has been administered intravenously without increased risk of adverse effects. Haloperidol, reviewed 11/02 Adverse Effects 1. 2. 3. 4. Cardiac: Hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, EKG changes (QT interval prolongation) Heme: Mild and transient leukopenia CNS: Extrapyramidal Symptoms (incidence is significantly lower with IV administration than with oral administration): parkinsonian-type movements, akathisia, and dystonic reactions Tardive Dyskinesias: persistent rhythmic involuntary movements- symptoms continue despite discontinuation of medication Misc: laryngospasm, bronchospasm Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (characterized by hyperpyrexia, severe hypertonicity of skeletal muscles, diaphoresis, tachycardia, alterations in blood pressure, and arrhythmias). Syndrome can be fatal, haloperidol should be discontinued immediately and supportive care established. Comments 1. 2. 3. 4. Haloperidol lowers the seizure threshold in patients with history of epilepsy and those patient in acute alcohol withdrawal. Haloperidol decanoate CANNOT be administered IV. If administering haloperidol, be sure haloperidol lactate is used. Haloperidol decanoate should be administered via deep IM injection. Concomitant use of haloperidol with other CNS depressants will produce additive effects. There is considerable interindividual variation in the dose of haloperidol required to control behavior. Doses should be titrated carefully and the lowest possible dose should be used to avoid adverse effects. haloperidol.wpd/page 2 12.97