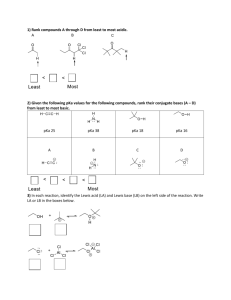
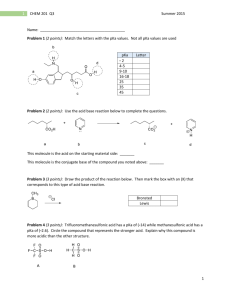
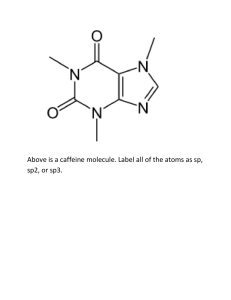
Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The relationship between
advertisement

Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) Can we predict the relative basicity of two bases ? Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) Can we predict the direction of equilibrium of the following reactions? Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) The relationship between structure (size) and acidity FHO- Cl- s e s a re c In y it il b ta S Br- B a HS- I- HSe- The extent of electron delocalization (overall size) of the corresponding conjugate bases may correlate with the acidity. Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) The relationship between electronegativity and acidity Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) The relationship between structure / electronegativity and acidity Predicting the Strength of Acid / Base The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base. (The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base) The relationship between structure / hybridization and acidity *The higher the s-character, the higher is the carbon’s electronegativity. H H C C H C C H H H H H H H C C H H H H Acidity Increases H H C C C C H H H Basicity Increases C C H H The Strength of Acid / Base: pKa The Strength of Acid / Base: Inductive Effect Inductive Effect: propagation of bond polarity through σ-bond network (decrease with the distance) The Strength of Acid / Base: Resonance Effect requires energy for the change endothermic Resonance Effect: stabilization of the system by having resonance structures (increase with the # of equivalent resonance structures) pKa vs. ΔG° (Standard Free-Energy Change) requires energy for the change endothermic ΔG° = −RT ln Keq pKa = −log Ka ΔG° = 2.303RT (−log Ka) = 2.303 (8.314x10-3 kj/mol°K) x (273+25)°K (−log Ka) = (5.7 kj/mol) x 4.75 = 27.1 kj/mol Resonance Effect: stabilization of the system by having resonance structures (increase with the # of equivalent resonance structures) Organic Compounds as Bases carboxylic and and alcohol as acids carboxylic as a base H O O H H3C O + H Cl H H3C O + Cl- The Strength of Acid / Base: pKa Mechanism for Organic Reactions Why acid–base? Step 1 Many reactions in organic chemistry are: either acid–base reaction themselves or involves acid–base reaction at some stage Mechanism for Organic Reactions Why acid–base? Many reactions in organic chemistry are: either acid–base reaction themselves or involves acid–base reaction at some stage Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Acid / Base in Nonaqueous Solution Leveling Effect: No stronger base than OH- can exist in water. Synthesis of Tritium-labeled Compound