Finding the Open Circuit Time Constants
advertisement

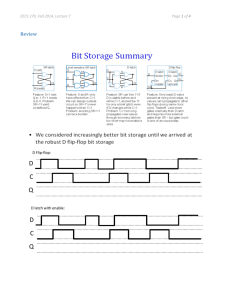
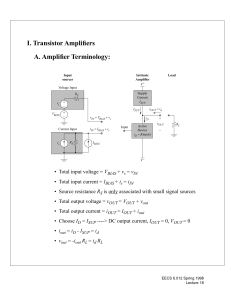
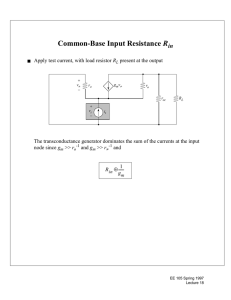
I. Finding the Open Circuit Time Constants τj’s A. Example: CE Amplifier V+ iSUP iOUT RS + + V − s RL vOUT − + V − BIAS V− • Small signal model Cµ RS + + Vs + − rπ Vπ gmV π Cπ − ro roc RL Vout − (a) EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 B. Procedure • Eliminate all independent sources (e.g., Vs --> 0) • Open-circuit all capacitors • Find Thevenin resistance by applying it and measuring vt. C. Time Constant for Cπ RS Cµ --> 0 rπ + vt ↓ Cπ -> 0 it gmVπ ro || roc RL _ • Result: (by inspection) R Tπ = R s r π τ C πo = R C Tπ π EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 D. Time Constant for Cµ • Same procedure: + vt ↓ _ RS io Vo ↓ it + Cµ --> 0 rπ Vπ gmVπ Cπ -> 0 ro || roc RL _ • Let R’in = Rs || rπ and R’out = ro || roc || RL − vt + R'in = RS r π + it gmv π vπ R'out = ro roc RL − vt + vπ i t = ---------------- + g m v π R′ out v π ---------- = – i eliminate vπ t R′ in v t ---- = R = R′ + R′ 1 + g R′ Tµ out in m out i t τ C µo = R C = Tµ µ R′ out + R′ 1 + g R′ C in m out µ EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 E. Dominant Pole for CE Amplifier • Sum Individual time constants b 1 = ( R Tπ C π + R Tµ C µ ) b 1 = R′ C + R′ 1 + g R′ C + R′ C in π in m out µ out µ • Assume τ1 >> τ2 b1 = τ1 + τ2 ≈ τ1 ω 1 1 ≈ ------ = ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3dB b R′ C + R′ 1 + g R′ C + R′ C 1 in π in m out µ out µ • Very similar result to the Miller effect calculation • Addtional term R’outCµ is taken into account EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 II. Common Collector Frequency Response V+ + RS RL + V − s vOUT − iSUP + V − BIAS V− A. Small Signal Model • Add Cµ and Cπ to the two-port model from Chapter 8 Cπ RS Vs + − E B Rout + + Vin Rin Cµ − + − Vin RL Vout − C EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 B. Low Frequency Voltage Gain R v R in L out ----------- = ---------------------- ( 1 ) -------------------------- v R S + R in R L + R out s • Substituting values for input and output resistance R v rπ + βo R L L out ----------- = ---------------------------------------- ( 1 ) ----------------------------------------------------------------R +r +B R R + 1 ⁄ g + R ⁄ β v S π o L L m S o s C. Use Miller Approximation to Find Dominant Pole • Voltage gain from B to E across Cπ A R R L L = -------------------------- = ---------------------------vCπ R +R 1⁄g +R out L m L • Total Capacitance seen at the input CT = (1-AvCπ)Cπ + Cµ C 1⁄g m +C = C ---------------------------------T π 1 ⁄ g + R µ m L • Thevenin resistance seen by CT RT = RS || Rin EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 D. Common Collector Dominant Pole • The dominant time constant for a CC amplifier is C π τ = R || R ------------------------ + C in 1 + g R µ S m L • Substitute for Rin and look at ω3dB ω 3dB 1 = ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------C π R || r + β R -----------------------+C o L 1 + g R µ S π m L • Effect of Cπ is small • In general RS < Rin---> frequency response is dominated by RSCµ EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 III. Common Base Amplifier Frequency Response V+ iSUP iOUT RL Is IBIAS RS V− A. Small Signal Model E C Iout Is RS Rin −Iin π C Rout Cµ RL B • DC Gain R i R out S out ---------- = ---------------------- ( 1 ) -------------------------- i R in + R S R L + R out s EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22 B. Use Method of Open Circuit Time Constants • Thevenin resistance across Cπ R Tπ = R || R = R || 1 ⁄ g ≈ 1 ⁄ g S in S m m • Thevenin resistance across Cµ R Tµ = R out || R ≈ β r || R ≈ R L o o L L • Summing the open circuit time constants and taking reciprocal ω 3dB 1 ≈ ----------------------------------------------C ⁄g + R C L µ π m IV. Summary of Frequency Response of Single-Stages CE/CS: with voltage output - suffers from Miller effect CE/CS: with current output - “wideband” CB/CG: “wideband” CC/CD: “wideband” • “Wideband” means that the stage can operate near the frequency limit of the device ... fT • Frequency limitation is set by external circuit RS and RL EECS 6.012 Spring 1998 Lecture 22