Tutorial 9: Using Sinusoidal Inputs in PSPICE
advertisement

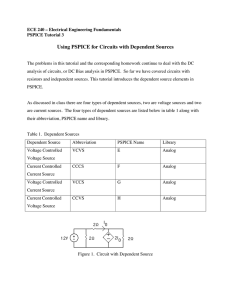
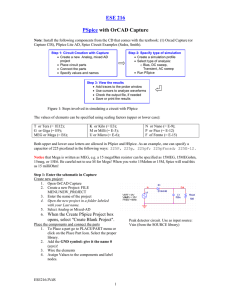
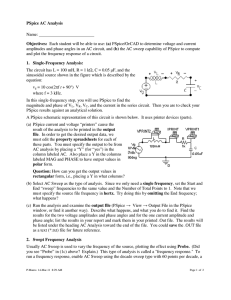
ECE 240 – Electrical Engineering Fundamentals PSPICE Tutorial #9 Using Sinusoidal Inputs in PSPICE In this tutorial, we will review the use of PSPICE to simulate a circuit with a sinusoidal input. Figure 1 shows the PSPICE schematic for a circuit that was analyzed in class. The original circuit had a sinusoidal input 9 cos 2t. Note the use of the VSIN source for this input. The VOFF is set to zero. The VAMPL is set to 9. The FREQ is set to the frequency in Hz. For this source the frequency in Hz is 2/(2π) = 1/π = 0.3183. R1 3 VOFF = 0 VAMPL = 9 FREQ = .3183 1 L1 R3 2 2 1 V V1 1 R2 1 L2 .5 1 C1 I .25 0 Figure 1. PSPICE Schematic Probes are placed in the circuit to measure the voltage across the resistor and the current through the inductor. Since we want to plot the voltage and current versus time, the Transient analysis is used. The Simulation Settings are shown in Figure 2. Note that the period of the input waveform is approximately 3 seconds. Thus, TSTOP was set to 9 seconds to provide a display of approximately 3 cycles. Another important difference is that the SKIPBP box was NOT selected. In this case PSPICE will let the circuit run to steady state BEFORE producing the plot. Thus, the solution will correspond to the steady state solution that we found in class. The method of phasors only produces the steady state solution. The transient part of the solution (homogeneous solution) will not appear. Figure 2. Simulation Settings for Steady State Analysis The results of the simulation are shown in figure 3. As expected, the voltage and current produced have the same frequency as the input. They only vary in amplitude and phase. Compare these results to the ones obtained in class. 2.0 0 -2.0 0s V(R3:2) I(L2) 2s 4s 6s Time Figure 3. Voltage and Current Waveforms 8s 10s