I. Dalton’s Law
advertisement

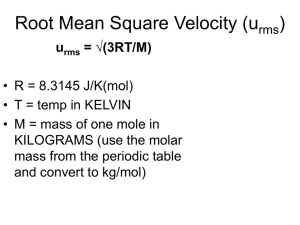
Dalton’s Law I. A. The total pressure of a mixture of gases equals the sum of the pressures each gas would exert independently 1. Ptotal = P1+ P2 + … 2. Partial pressures is the pressure a gas in a mixture would exert if it were alone in the container 3. Particularly useful for determining the pressure a dry gas collected over water: Ptotal = Pwet gas = Pgas + Pwater 4. B. P1 Ptotal Pwater vapor depends on the temperature, look up in table Combining Dalton’s Law and Ideal Gases 1. We can assume each gas will behave ideally in the mixture n RT n 2 RT P3 3 V V n RT n 2 RT n 3 RT RT RT P1 P2 P3 ... 1 (n 1 n 2 n 3 ) n total V V V V V n 1RT V 2. P2 It’s the total number of particles present that is important a. The volume of the individual particle is very small b. The forces among particles are very small C. Problems 1. Example: 46L He and 12L O2 at 25 oC and 1atm are pumped into a 5.0L tank. What are the partial and total pressures? a. Calculate the number of moles of each gas from the ideal gas law nHe 1.0atm46L PV 1.9mol RT 0.08206Latm / molK 298K nOx 1.0atm12L PV 0.49mol RT 0.08206Latm / molK 298K b. Calculate partial pressures of each gas from new conditions PHe nRT 1.9mol 0.08206lat / molK 298K 9.3atm 5.0L V POx 0.49mol 0.08206lat / molK 298K 2.4atm 5.0L c. Add partial pressures: 9.3atm + 2.4atm = Ptot = 11.7atm 2. Mole fraction = c1 = moles of molecule 1 divided by moles total n1 V χ1 n P n total RT χ1 P1 (V/RT) P1 (V/RT) P2 (V/RT) P3 (V/RT) .... P1 Ptotal P1 c1PT 3. Example: Find cO2 if PO2 = 156torr in air at PT = 743torr. a. cO2 = PO2/PT = 156torr/743torr = 0.210 b. 21% of the air molecules are oxygen 4. Example: Calculate PN2 if cN2 is 0.7808 when PT = 760torr. PN2 = cN2 x PT = (0.7808)(760torr) = 593torr 5. Example: 0.650L of gas at 22 oC is collected over water in the decomposition reaction of KClO3. Calculate PO2 in this gas and the amount of KClO3 in the reaction. PH2O= 21torr at 22 oC. PT = 754 torr a. 2KClO3(s) -------> 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) b. Find PO2 from Daltons Law: PO2 = PT – PH2O = 754-21 = 733torr c. Use ideal gas law to find moles O2 n 0.964atm0.650L 0.0259mol PV RT 0.08206Latm / molK 295K d. Calculate moles KClO3 needed to make this O2. 0.0259mol O2 2mol KClO 3 0.0173mol KClO 3 122.6g 2.12 g KClO 3 3mol O 2 mol II. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases A. Empirical Laws 1. Gas Laws we have just studied 2. Describe how gases behave, but don’t explain why they behave that way B. Theory or Model 1. Explains why gases behave as they do 2. Describing an Ideal Gas with the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) a. Gas particles very small compared to distance between them (assume gas molecules have no volume) b. Molecules constantly and rapidly move in a straight line until they bump into each other or the wall (this causes pressure) 3. C. c. Assume that the gas molecules’ attraction for each other is negligible d. Average kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature (K) Real gas molecules do have volumes, do attract each other Test: can the theory predict the experimental observations of PV = nRT? 1. Pressure is inversely proportional to Volume (Boyle’s Law) a. KMT: Decrease in Volume means particles hits wall more often b. This results in an increase in Pressure 2. Pressure is directly proportional to Temperature a. KMT: As temperature increases, gas speed increase b. Pressure increases as the collisions with the wall are harder 3. Volume is directly proportional to Temperature (Charles’s Law) a. KMT: As temperature increases, gas speed increase b. If pressure is to remain the same, the volume must increase 4. Volume is directly proportional to number of moles (Avogadro’s Law) a. KMT: As moles increases, more collisions with the walls occur b. If pressure is to remain the same, the volume must increase 5. Mixtures of Gases (Dalton’s Law) a. KMT: Identity of the gas molecule doesn’t change (ideal) properties b. Adding another gas increases pressure same as adding first gas D. Ideal Gas Law—Derivation from KMT 1. Physics (NA = Avogadro’s number, m = mass of particle, m = velocity) nN A 1 mμ 2 2 1 2 P (KE)avg N A mμ 2 3 V 2 2 n KEavg PV 2 P KEavg 3 V n 3 2. KMT: average KE is directly proportional to T(K) PV PV T RT n n E. The Meaning of Temperature 1. KMT: average KE is directly proportional to T(K) PV 2 3 2. RT (KE)avg (KE)avg RT n 3 2 F. Root Mean Square Velocity 2 μ rms μ 1. Root mean square velocity = mrms 2. Deriving an expression for mrms a. 1 3 3RT (KE)avg N A mμ 2 RT μ 2 μ rms NAm 2 2 b. particles kg kg (NA )(m) c. μ rms mol 3RT M 3RT NAm particle mol M molecularmassin kg R 8.3145 J/Kmol needed to give m meters/second 3. Example: Calculate mrms for He at 25 oC. μ rms 3RT M 2 3(8.3145 J/Kmol)(298K) 6 6 kgm 3 1.86 x 10 J/kg 1.86 x 10 1.36 x 10 m/s 2 (4g/mol)(1kg/1000g) kgs 4. Range of velocities of a gas sample a. Mean free path = avg. dist. between collisions ~ 1 x 10-7 m at STP b. Many collisions produce large range of velocities c. 500 m/s ~ mrms at STP, but velocities are widely ranging d. Temperature greatly effects the distribution (KMT) G. Effusion and Diffusion 1. Effusion = movement of gas into vacuum through a small opening a. Example: Find ratio of effusion rate for H2 and UF6. b. Graham’s Law: Rate of effusion of gas1 M2 352.02 Rate of effusion of gas 2 M1 2.016 13.2 2. KMT: effusion depends on average velocity of the gas particles 3RT M1 M2 Rate of effusion of gas 1 μ rms for gas 1 Rate of effusion of gas 2 μ rms for gas 2 3RT M1 M2 3. Diffusion = mixing of gases a. NH3(g) + HCl(g) -------> NH4Cl(s) b. Expected speed of mixing would allow estimation of distances: Rate of effusion of gas NH3 Rate of effusion of gas HCl μ rms for NH 3 μ rms for HCl M HCl M NH3 36.5 1.5 17 c. Multiple collisions with air gases complicate the model of diffusion d. The ratio of distance traveled is < 1.5; mixing time is several minutes H. Real Gases 1. No gas is ideal, although most are close at low P and high T 2. Where does the KMT fail in describing Real Gases? 3. For an ideal gas, PV/nRT = 1 at all pressures and temperatures 203 K 4. Modifying the Ideal Gas Law a. Real gas molecules have volume, which reduces the Volume available b. An empirical constant b for each gas is determined P nRT nRT P' V V nb c. Real gas molecules attract each other, making Pobs < P’ d. The higher the concentration of particles, the larger the effect e. The number of interacting pairs depends on (concentration)2 i. N particles has N-1 partners ii. Divide by 2 to eliminate counting each pair twice N(N 1) N 2 2 2 f. n N concentration V Pobs n P'a V 2 The correction for V and P combine in van der Waals equation Pobs 2 2 nRT n n a Pobs a V - nb nRT V - nb V V g. a and b are varied until the best fit of observation is found h. Low pressure = large volume, where volume of particles is negligible i. High temperature = fast motion, where attractions are negligible III. Atmospheric Chemistry A. B. Components: N2 = 78%, O2 = 21%, Ar, CO2, less than 1%, H2O is variable Smog Production in the lower atmosphere 1. Burning fossil fuels produces NOx = NO and NO2 2. NO2 + light -------> NO + O 3. O + O2 -------> O3 ------> O2 + O* (high energy O atom) 4. O* + H2O -------> 2OH radicals 5. OH + NO2 -------> HNO3 (nitric acid) 6. OH + hydrocarbons -------> photochemical smog 7. Prevalent in urban areas; harmful to respiratory system 8. Combated by public transportation, cleaner burning fuels C. Acid Rain 1. S(in coal) + O2 -------> SO2 2. 2SO2 + O2 -------> SO3 3. SO3 + H2O -------> H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) 4. Harmful to buildings and organisms 5. Need to remove sulfur from coal (Scrubbing) a. CaCO3 -------> CaO + CO2 b. CaO + SO2 -------> CaSO3 (solid calcium sulfite)