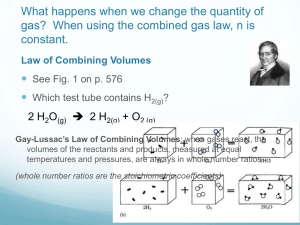
Study Guide Chapter 5 - Gases 1. Definition of pressure
advertisement

Study Guide Chapter 5 - Gases 1. Definition of pressure 2. Units of pressure 3. Conversion of pressure units 4. Temperature 5. What is absolute zero and what does it mean 6. Conversion between C and K 7. Gas Laws - problems dealing with all of the below Boyle PV=PV Charles V/T=V/T Avogadro V=an Put it all together you get PV=nRT R=0.08206 L atm/K mol 8. What is STP? 273, 1 atm 9. What is volume of gas at STP (22.42 L) 10.Combine stoichiometery and gas laws to calculate volume of gas evolved in a reaction 11.Tie between gas density and Molecular mass Molar mass = density RT/P Be able to use equation to go from density to molar mass 12. Partial pressures A. What is the law of partial pressure B. Can you handle mixtures of gases in calculations C. What is the mole fraction and how do you calculate it D. Why do you have to be careful about volumes of gases made in the lab using water? 13. KMT Theory A. What does KMT mean? B. Explain any of the basic gas laws using KMT theory and a diagram C. How is Kinetic Energy related to temperature D.Calculate root mean square velocity of a gas molecule urms = 3RT Molar Mass Note in above equation need to use R=8.314 J/K mol and answer is in m/s 14. What is effusion, diffusion (but no calculations) 15. Why would a gas behave in a non-ideal manner? 16. Given the proper equation(page 223) and constants a and b, calculate P for a real gas