PV = nRT Ideal Gas Law
advertisement

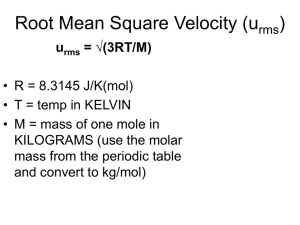
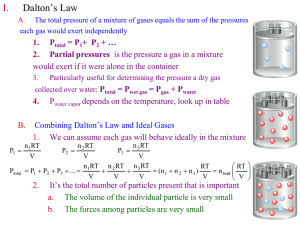
Chapter 5 Gases Chapter 5 Gases WHY? Sketch of Modern Balloons WHY? Mathematics V/T = constant 1.00 PSI 8.00 PSI 8.00 PSI WHY? Mathematics PV = constant Mathematics V/n = constant •(n = moles) Moles 273 K 1.00 ATM 804 K 9.79 ATM (atm) Mathematics P/T= constant Mathematics Summary V/n = constant V/T = constant P/T = constant PV = constant Mathematics Summary V/nT = constant P/T = constant PV/nT = constant Mathematics PV/nT =Summary constant PV = nTconstant •constant =R PV = nRT Ideal Gas Law Conditions of Use PV = nRT Ideal Gas Law •P units must be atm’s •V units must be liters •T must be in Kelvin Gas Law Resources Pressures equivalent to the standard 1.00 ATM 28.3 ft. H2O 29.92 in. Hg 76.0 cm Hg 760.0 mm Hg 760.0 torr 14.7 psi. Practice • Fill out the following chart. • mm Hg. atm. kPa. • • • . . . 1215 0.714 143 bar Gas Law Resources Temperature - must be absolute - never negative • • Temperature must be in Kelvin K= oC + 273 Practice • Calculate the volume of 1.0 mole of a gas at Standard Temperature and Pressure. Practice • Fill out the following chart for C H • Press. Vol. Temp. Moles Grams 4 • • • 1.75 L . . 0.895 atm 433 mm Hg 19 oC 6.0 oC 92.4 mL 1.74 bar . 8.66 L 14.0 0.395 . • 1.66 310 K 10 Experiment Experiment Experiment 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 Fe + N2 NR Interpretation • Air contains both N and O • Each gas has its own independent 2 2 pressure. • “The sum of all individual gas pressures in a gas mixture is equal to the total pressure” DALTON • Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures (go to video) KMT •Kinetic Molecular Theory of gases Gases consist of very tiny particles in continuous random motion. Particle collisions are elastic(no energy lost). Particle volume is negligible. Particle interaction is negligible. •molecular speed causes both pressure and volume of gases Graham’s Law • Often called Grahams’ Law of Diffusion - in error • Diffusion - movement of gas down an open tube • complex and influenced by many factors. • Effusion - movement of gas through small holes. • Graham’s Law of Effusion of Gases • “At a given temperature and pressure, gaseous effusion rate in moles per time unit, is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of the gases”. • effusion rate of B • effusion rate of A = Ideal vs Real • Review KMT. Obvious non-realities. • Some gas molecules are NOT tiny. • Many gas collisions DO lose energy • Gas molecules HAVE a noticeable volume • Some molecules have SIGNIFICANT interaction.