Content Benchmark P.8.B.3
advertisement
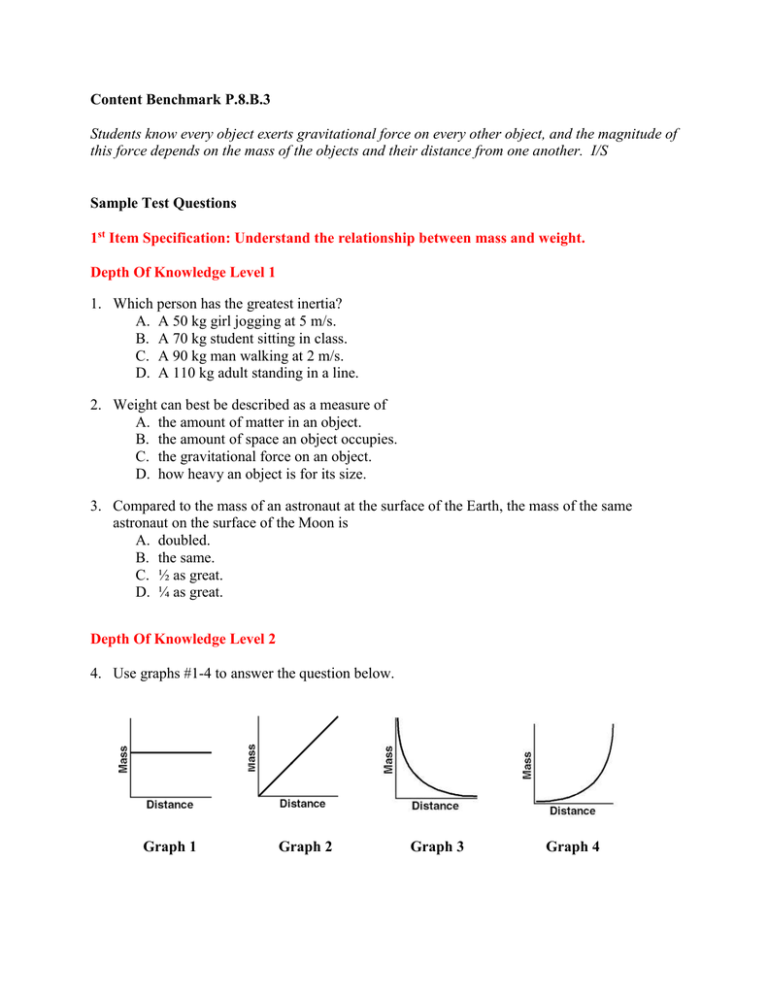
Content Benchmark P.8.B.3 Students know every object exerts gravitational force on every other object, and the magnitude of this force depends on the mass of the objects and their distance from one another. I/S Sample Test Questions 1st Item Specification: Understand the relationship between mass and weight. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which person has the greatest inertia? A. A 50 kg girl jogging at 5 m/s. B. A 70 kg student sitting in class. C. A 90 kg man walking at 2 m/s. D. A 110 kg adult standing in a line. 2. Weight can best be described as a measure of A. the amount of matter in an object. B. the amount of space an object occupies. C. the gravitational force on an object. D. how heavy an object is for its size. 3. Compared to the mass of an astronaut at the surface of the Earth, the mass of the same astronaut on the surface of the Moon is A. doubled. B. the same. C. ½ as great. D. ¼ as great. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 4. Use graphs #1-4 to answer the question below. Graph 1 Graph 2 Graph 3 Graph 4 Which graph best represents the relationship between the mass of an object and its distance from the center of the Earth? A. Graph 1 B. Graph 2 C. Graph 3 D. Graph 4 5. The graph below shows the weight of three objects on the Moon as a function of their mass. Weight (N) Weight v Mass on Moon 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Mass (Kg) The acceleration due to gravity on the Moon is approximately 1.6 m/s2. A fourth object was found to have a weight of 144 Newtons, what would be the mass of this object? The mass would be A. 144 Kg, because mass and weight are the same on the Moon. B. 115 Kg, due to the low acceleration of gravity on the Moon. C. 90 Kg, due to the low acceleration of gravity on the Moon. D. 0 Kg, because objects are weightless on the Moon. 2nd Item Specification: Explain the relationship between gravity and the motion of falling objects. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 6. Astronauts on the orbiting space station 335 Kilometers above Earth appear to be weightless because A. there is no gravity in space so they do not weigh anything. B. space is a vacuum and there is no gravity in a vacuum. C. they are too far from Earth to have weight. D. the astronauts are in a state of free fall. 7. For a falling skydiver, terminal velocity is reached when the A. upward force of air resistance is greater than the downward force of gravity. B. upward force of air resistance is equal to the downward force of gravity. C. downward force of air resistance is greater than the upward force of gravity. D. downward force of air resistance is equal to the upward force of gravity. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 8. An 800 Newton person is standing on a scale in an elevator. If the elevator cable breaks and the elevator, person, and scale are in free fall, the person would experience a weight of A. 400 N, accelerating downward. B. 0 N, accelerating downward. C. 800 N, moving downward at a constant speed. D. 0 N, moving downward at a constant speed. 9. Use graphs #1-4 to answer the question below. Graph 1 Graph 3 Graph 2 Graph 4 Which graph represents an object falling at terminal velocity? A. Graph 1 B. Graph 2 C. Graph 3 D. Graph 4 3rd Item Specification: Identify and describe qualitatively the relationship between gravitational force, mass, and distance (Universal Law of Gravitation). Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 10. If the Earth were twice as massive as it is now, then the gravitational force between it and the sun would be A. four times as great. B. the same. C. twice as great. D. half as great. 11. When a satellite is a distance r from the center of Earth, the force due to gravity on the satellite is F. When the satellite’s distance from the center of Earth is increased, the gravitational force A. increases. B. decreases. C. remains the same. D. increases then decreases. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 12. Use graphs #1-4 to answer the question below. Graph 1 Graph 3 Graph 2 Graph 4 Which graph best represents the relationship between gravitational force and distance from Earth for an object traveling away from Earth? A. Graph 1 B. Graph 2 C. Graph 3 D. Graph 4 13. In each diagram below, the mass of two objects is labeled. These masses are separated by a radius. Which diagram would produce the greatest gravitational force between the two objects? A. Diagram 1 B. Diagram 2 C. Diagram 3 D. Diagram 4 Constructed Response P.8.B.3 1. The data in the table below records the weight of an object at five equal distances from Earth. Location 1 is taken at Earth’s surface. Location (#) 1 2 3 4 5 Distance (Earth Radii) r 2r 3r 4r 5r Force (Newton) 500 N 125 N 56 N 31 N 20 N Location # A. What is happening to the mass of the object as it is taken from Location 1 to Location 5? B. Plot Force versus Location for the five locations from the data table. Label the x and y-axis with the appropriate labels and units, and provide a graph title. C. Using your graph, explain and justify what is happening to the weight of the object as the object is taken from Location 1 to Location 5. Content Benchmark P.8.B.3 Students know every object exerts gravitational force on every other object, and the magnitude of this force depends on the mass of the objects and their distance from one another. I/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 1. D, DOK level 1 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. A, DOK level 2 5. C, DOK level 2 6. D, DOK level 1 7. B, DOK level 1 8. B, DOK level 2 9. A, DOK level 2 10. C, DOK level 1 11. B, DOK level 1 12. D, DOK level 2 13. A, DOK level 2 Constructed Response 3-point Answer and Score Rubric: Force v. Location 600 Force (N) 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 2 4 6 Location (#) 3 points Response addresses all parts of the question clearly and correctly. Mass is a property of matter that does not depend upon location in a gravitational field. Mass of the object remains constant. Student graph shape matches the key with graph title, and correct labels for both xaxis and y-axis. Weight decreases rapidly with distance as shown in the downward sloping graph. Weight depends on location. As distance increases, weight decreases. The strength of the gravitational field decreases with distance resulting in less weight. 2 points Response addresses all parts of the question and includes only minor errors. 1 point Response does not address all parts of the question. 0 points Response is totally incorrect or no response provided.







