Creation of Israel
advertisement

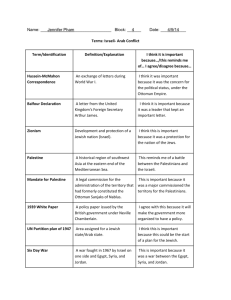
VI. Creation of Israel A. Jewish and Arab nationalists both wanted to END the British mandate of Palestine. Due to anti Semitism, Zionism became a popular movement. Zionism - Establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine B. Theodor Hetzel created an organization which encouraged Jews to migrate to Palestine. They even called on Britain and other European nations for support. 2. It started a wave of anti-Semitism 1. The Dreyfus Affair A Jewish captain in the French army, Alfred Dreyfus was tried in 1894 on a trumped-up charge of spying for Germany. in France. The entire Jewish community was suspected of disloyalty. Synagogues were desecrated and individual Jews were attacked. C. As international pressure increased to create a Jewish state, Lord Balfour of Great Britain sent a letter to a Zionist leader. "The Balfour Declaration.“ The Balfour Declaration enraged Palestinian Arabs who outnumbered the Jewish settlers. The Arabs started to call for their own independent state. D. The Great Depression of the 1930's did not improve conditions and many were moving to Palestine. The demand for an independent Jewish state increased after the Holocaust. E. In Palestine, Zionist groups tried to establish Jewish settlers. 1. Zionist groups helped Jews buy land from Arabs. a. The Arabs sold the land because many had moved to the city. 2. Arab tenant farmers were forced to leave. a. When the Arab farmers sold the land, the tenant farmers had to vacate. Jewish homes throughout the world kept Jewish National Fund boxes, PUSHKEH. By 1947 more than half of the total Jewish holdings in Palestine came from these funds. F. The newly formed United Nations tried to keep order in Palestine. The UN divided the area into two zones. One zone was Arab and the other Jewish. Many Palestinians were upset about losing parts of their homeland. It led to an increase in Pan Arabism. Population of Palestine Year 1883 1914 1922 1931 1939 1946 Jewish 15,300 61,000 95,000 176,000 458,000 603,000 Arab 356,000 737,000 726,000 881,000 1,083,000 1,340,000 Partition Plan November 29, 1947 United Nations Partition Plan, 1947 Tan: Jewish state Grey: Arab state White: International zone Holy City of Jerusalem The Western Wall Dome of the Rock Church of the Holy Sepulcher G. Armed conflicts over Israel 1. 1948-49: War after creation of Israel- The independent state of Israel was declared on May 14, 1948. One day later, united Arab neighbors declared war on Israel. 2. 1967: “Six-Day War” a) Preemptive war to create protective buffer around Israel b) Tripled Israeli territory in six days c) Placed 1.5 million Palestinians under Israeli rule 3. 1973: “Yom Kippur War” a) Egypt and Syria attack unsuccessfully in Sinai and Golan Heights b) An oil embargo was placed on Western nations that supported Israel. Oil prices increased drastically. **Oil Crises of 1973** A. The Oil Crises of 1973 is an example of the impact OPEC has on the international community. The Yom Kippur War which involved Israel against Egypt and Syria had just started. OPEC supported the Arab nations in the war. What could OPEC do to impact western nations? • Supporters Israel could not buy oil. • Increased price per barrel • Increased inflation INFLATION - Increasing consumer prices over a period of time causing the value of money to decrease Gas lines in New York during 1973 The western nations then imposed an embargo of the OPEC nations. EMBARGO – Not permitting trade and commerce with a particular nation. ended the war and the oil crises. OPEC became less uniform. Some were producing more than the agreed amount. OPEC focused on countries that were producing too much oil, what could be done? • Negotiate new prices • Take over the country Jimmy Carter – US President Anwar Al Sadat – Egyptian President Menachem Begin – Israeli Prime Minister September 17, 1978 **The Palestinian Liberation Organization** [PLO] • Created in 1964 as a government in exile • Leader: Yasir Arafat [d. 2004] • 1974: PLO recognized by the U.N. as representative of the Palestinian people • 1987 and 2000 used strategy of intifada [uprising] to oppose Israeli rule • Became Palestinian Authority 1993; current leader Mahmoud Abbas H. Other Armed conflicts over Israel? Refer to BBC activity/notes Where are the Palestinians? The largest group of refugees in the world today. Israel: 1 million Jordan: 1.5 million Gaza: 825,000 West Bank: 583,000 Saudi Arabia: 123,000 Iraq: 90,000 Syria: 383,200 Lebanon: 376,500 Egypt: 40,000 N. Africa: 13,000 Kuwait: 35,000 80% left in 1948. 44% of Jordan’s population are displaced and refugee Palestinians Israel rejects the “right of return” for refugees. I. Attempts at Pursuing Peace A. U.N. Resolution 242 (1967) 1) Called for withdrawal of Israeli forces from territories occupied in 1967 2) Called for Israel, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan to recognize one another B. Separate peace agreements between Israel and Egypt (1978) and Israel and Jordan (1994) C. Oslo Agreement (1993) “Land for Peace” 1) Palestinians abandon armed struggle and accept Israel’s right to rule over 78% of mandate Palestine 2) In return they receive the remaining 22% (West Bank, Gaza, Arab East Jerusalem) D. U.S. Policy- George W. Bush: 2002 “two-state solution” J. Continuing Conflict 1) Hamas, Hezbollah, and other extremist groups reject right of Israel to exist and reject all negotiations with Israel 2) Violent acts on both sides invite violent reprisals, continuing the cycle of violence 3) Western Wall and Jewish settlement in West Bank 4) Gaza: Palestinian state or “prison?” **Hezbollah** • Created in 1964 as a government in exile • Leader: Yasir Arafat [d. 2004] **Hamas** • Created in 1964 as a government in exile • Leader: Yasir Arafat [d. 2004] Arab-Iraeli Conflict EXIT TICKET • If you are a conservative Israeli, what you want? • If you are a conservative Palestinian, what do you want? • What do YOU think should be done to finally solve this conflict?