Chapter 2-- Study Guide Figure (section-ending) questions It
advertisement

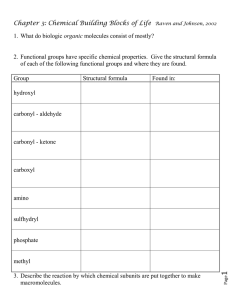
Chapter 2-- Study Guide 1. Critically read Chapter 2 pp. 59-69 before “ENZYMES AND METABOLISM” section 2. Comprehend Terminology (those in bold in the textbook) 3. Study-- Figure questions, Think About It questions, and Before You Go On (section-ending) questions 4. Do end-of-chapter questions: – Testing Your Recall— 6 to 10, 15-17 – True or False– 1 3, 5, 6, 7 1 § 2.4 Organic Compounds 2 § Organic compounds — • • Def.--Compounds of carbon The organic molecules of life— 4 groups: carbohydrates, lipids, . . . • Functional groups of organic molecules— a group of atoms that determines the functional characteristics of an organic molecule • For example– Fig. 2.14 3 (See next slide) 4 ATP (adenosine triphosphate) ̶ A Nucleotide three _______________ groups Base; adenine Sugar; ribose 5 § Monomers and polymers — • • • Polymers– molecules made of a repetitive series of identical or similar ___________ For example, starch is a polymer of about 3,000 glucose monomers Mechanism (how?) by poly ____ – this above process; also called dehydration synthesis (OR condensation) Fig. 2.15 6 Which is polymerization reaction, A or B? A. B. Give an example of polymerization. 7 § Carbohydrates — • • • Hydrophilic molecules– Why? General formula (CH2O)n 1. Monosaccharides (simple sugars)— glucose, fructose, and galactose; isomers of each other (C6H12O6) Fig. 2.16 8 Where are carbon atoms? Fig. 2.16-- Three monosaccharides; hydroxyl groups? Disaccharides-next slide 9 Glucose + Fructose 2. Disaccharides Milk sugar A product of starch digestion 10 3A. Polysaccharide– long chains of glucose (Glucose, glu.) Starch and cellulose next slide Glu. Glu. Glu. Glu. Can we make glycogen? Glu. Glu. 11 § Carbohydrates (continued)— • • • • 3B. Other polysaccharides– Starch—energy-storing molecules in plants; when sunlight + nutrients is not available, plants use starch as energy C____________—structural molecule of cell walls; can we digest it? Why? For example, wood, cotton etc. 12 § Carbohydrates (continued)— • 4. conjugated carbohydrates– • • • Bound to proteins (a) & lipids (glycolipids, cell surface coat) Example— a. glycoproteins; major component of mucus; where? b. Proteoglycans– hold cells and tissues together; gelatinous filler in the eye; in the joints etc. 13 Review Table 2.6, a summary of carbohydrate functions: 1. Monosaccharides 2. Disaccharides 3. Polysaccharides 4. Conjugated carbohydrates 14 § Lipids — • • • Hydrophobic molecules; Why? Include C, H, and O; with high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen Ex. C57H110O6 (tristearin) vs. (CH2O)n Less oxidized than carbohydrates; more calories per gram • Several major types of lipids in humans Table 2.7 15 Steroids 16 Glycerol Is this a dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis reaction? 1.--3 Fatty acids 2.--Triglyceride synthesis 17 Next slide 3.--Fig. 2.20 Lecithin, a phospholipid 18 Fig. 2.20c– A simplified representation of the phopholipid molecule Why is a phospholipid amphiphilic? 19 4.--Fig. 2.21 A prostaglandin, Eicosanoids •Five of the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. •Functions-- 20 5.—Fig. 2.22 Cholesterol All steroids have this basic fourringed structure. Functions—? Next slide 21 5.--Cholesterol — 1. (Where?) Cholesterol is found only in animals (natural product); from where? 2. Related to cardiovascular disease (INSIGHT 2.3—Good and bad cholesterol; p. 76) 3. Function-– – Precursor of steroids Important component of cell membrane 22 § Amino acids & proteins — • • • • A protein is a polymer of amino acids A amino acid has a central carbon atom with an amino and a carboxyl group bound to it The radical (R) group makes each of the 20 amino acid unique Essential a.a.--? Fig. 2.23 23 Similarities of all a.a.? R groups 24 § Amino acids & proteins (continued)— • Joining of amino acids– by peptide bonds– to form peptides Fig. 2.23, 2.25 25 a.a. #2 Is this a dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis reaction? 26 § Protein structure Fig. 2.25 primary structure of insulin 27 28 § Amino acids & proteins (continued)— • Tertiary structure– folding into globular and fibrous shapes – – Globular proteins– a ball of yarn; Ex. enzymes and antibodies Fibrous proteins– slender filaments; muscle contraction proteins-- 29 § Protein functions— 1. Structure– Keratin gives strength to nails, hair, and skin surface 2. Communication– oxytocin (a ligand) binds to a protein (its receptors) 3. Membrane transport channels— Sodium and potassium channels 4. Catalysis– enzymes etc. 30 Check Point Questions A. Use the simplified phospholipids (each with a head and two wavy tails) to construct a portion of a cell membrane. B. Point out the polar region and the nonpolar regions. 31