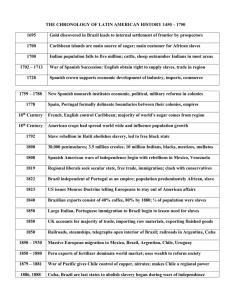
The visible hand of China in Latin America London Business School
advertisement

The visible hand of China in Latin America Opportunities, Challenges and Risks Javier Santiso Chief Economist & Deputy Director OECD Development Centre London Business School London June 2007 1 The cognitive effect: new emerging capitalisms. 2 The trade effect: the dark side of the boom. 3 China and India as a wake up call. 2 China: extraordinary or back to normal? China GDP (% of world total) GDP in U$ (% of World GDP, 2005) 35 USA 30 Japan 25 Germany 20 U. Kingdom France 15 China 10 Italy 5 Spain 2045 2001 1950 1900 1870 30 1820 20 1700 10 1600 0 1500 0 Canada According to IMF estimates Chinese gross domestic product based on purchasing-powerparity (PPP) amounts to 13.6% of 2005 world GDP (20.7% in the case of USA). Source: OECD Development Centre Based on: International Financial Statistics and Angus Maddison, 2006. 3 The cognitive impact: The emergence of new capitalisms. Center and Periphery rebalanced… GDP share of world output (WEO, 2005) Emerging China Asia 5.0% 9.1% Korea&Japan 12.0% Asia represents more than one fifth of world output. US 28.0% EU 30.3% LatAm 4.7% 4 China has doubled its GDP in 8 years…without the help of Money Doctors! GDP in constant prices U$ Millions 12000 10000 Brazil China Japan Mexico Korea China 8000 6000 4000 2000 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 0 Source: Datastream (Economist Intelligence Unit) Chinese growth rates has been higher than those observed in Brazil and Mexico during their glorious years. 5 1 The cognitive effect: new emerging capitalisms. 2 The trade effect: the dark side of the boom. 3 China and India as a wake up call. 6 Are raw material prices facing a Chinese shock? Commodities Prices in real terms 140 120 China? Is China to blame for commodities prices? 100 80 60 40 1900 1915 1930 1945 1960 1975 1990 2005 Source: OECD Development Centre. Based on Oxford Latin American Economic History Database and Thomson Datastream, 2007. 7 Latin America is endowed with natural resources and dependent on the commodities’ cycle LATIN AMERICA'S PERCENTAGE OF COUNTRIES' EXPORTS Commodities % of country's exports Oil 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Agriculture & other Venezuela Chile Peru Argentina Colombia Brazil Latin America Mexico Source: OECD Development Centre, 2007. Based on: National Balance of Payments, 2005. 8 Whereas exports with the US are stable, countries are increasingly sensitive to China EXPORTS TO U.S. AS PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL EXPORTS Exports to US as % of Total . 1995-2005 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1995 Argentina Brazil Chile Mexico China India 2005 Indonesia Korea Philippines Asia Latin America EXPORTS TO CHINA AS PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL EXPORTS Exports to US as % of Total . 1995-2005 1995 25 2005 20 15 10 5 0 Argentina Brazil Chile Latin America Mexico India Indonesia Korea Philippines Asia Source: OECD Development Centre, based on IMF Trade Statistics, and OECD Trade Directorate, 2007. 9 Latin America is tackling its vulnerability to US slowdown by diversifying exports LATIN AMERICA: EXPORTS TO CHINA AS PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL EXPORTS 1999 2005 Chile Peru Argentina Brazil Colombia Venezuela Ecuador Mexico 0 2 4 6 8 Percentage 10 12 14 Source: OECD Development Centre and UNCTAD, 2007. 10 1 The cognitive effect: new emerging capitalisms. 2 The trade effect: the dark side of the boom. 3 China and India as a wake up call. 11 A trade wake up call: Is China’s trade integration: a bonanza or a threat? * Asian countries competition vs. Chinese exports to US, % 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 60% Latin American countries competition* vs. Chinese main export products 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% a *Value of exports to US from China in same product categories as country´s exports, as % of country´s total exports to US Source: C.HJ.Kwan, Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research *Arithmetic average of the following indexes: CC= n (a n n it ) 2 n it n a jt (a n jt ) 2 and CS= 1 - 1 2 a n it - a njt n n where ajt and ait equals the share of item “n” over total exports of countries j (China) and i in time t. Source: Blázquez, Rodríguez and Santiso (2006) 12 Diversification is a concern for Latin America’s competitiveness… Latin America Herfindahl-Hirschmann Index by Destination 2005 Brazil Argentina Chile Uruguay Dominica Guyana Peru Paraguay Nicaragua Bolivia Colombia Costa Rica Panama Ecuador Guatemala Honduras Venezuela Belize 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Mexico HH Index 2000 Source: OECD Development Centre. Based on CEPAL (2006) and World Trade Integrated Statistics. 13 Product specialisation has increased recently in the region… Latin America Herfindahl-Hirschmann Index by Product 2005 Brazil Costa Rica Latin America Argentina Honduras Mexico Nicaragua Uruguay Colombia Guatemala Peru Guyana Bolivia Chile Paraguay Panama Belize T. and Tobago Dominica Ecuador 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Venezuela HH Index 2001 Source: OECD Development Centre. Based on CEPAL (2006) and World Trade Integrated Statistics. 14 A wake up for reforms: The proximity to export markets Mexico benefits from its geographic proximity to its major export markets: • Lower transport and communication costs • Access to FTA • Just-in-time delivery 24 Days 4 Days 160 Km 11,700 Km Shipping time Mexico is more competitive in manufacturing more sophisticated products which require frequent communication with the client or supplier and short reaction times. 15 Pending reforms : the upgrade of port facilities Container Handling Charges Cargo Mandatory Handing Price Fixed Cooperative Median Port Country World CMPCH LSU Services Restriction Agreements Agreements Clearance Efficiency Crime Index Bank Index Index Index Index Index Index time (Days) Index (1-7) (1-7) Singapore 1 0.38 0 0.33 2 6.76 6.72 US$/TEU 117 NA NA Hong Kong 0 0.25 0 0 NA 6.38 5.46 NA NA NA Taiwan 0.5 0 0 0 NA 5.18 4.49 140 163 NA Japan 0.75 0.13 0.89 1 NA 5.16 5.16 250 202 NA Malaysia 0 0.25 0 0.38 7 4.95 5.76 75 NA NA Spain 0 0.06 1 0 4 4.88 6.08 200 105 NA 0 0 0 NA 4.12 5.22 NA NA Korea 0.38 NA 0.5 0 0.38 4 3.98 5.12 93 NA Thailand 0.63 NA Argentina 0 0 1 7 3.81 4.52 NA 139 NA 0.13 0 0 0 NA 3.81 5.02 NA NA Vietnam 0.5 NA Chile 0 0.43 1 3 3.76 6.05 100 NA 0.25 202 China 0.5 0 0 0 7 3.49 4.44 NA 110 NA Indonesia 1 0 0.38 5 3.41 4.06 NA NA 0.06 NA Mexico 0.5 0 1 4 3.34 2.61 NA NA 0.38 NA Venezuela 0 0 1 1 11 3.28 3.63 NA NA NA El Salvador 0 0 0 1 4 2.95 2.3 NA NA 61 Brazil 0.5 0.75 0 1 10 2.92 4.45 328 292 NA 0 0.5 1 7 2.88 3.32 NA 142 NA Peru 0.5 0 0 0 1 NA 2.79 4.28 NA NA NA India 0.5 0 0 0.38 7 2.79 3.51 118 NA NA Philippines Ecuador 0 0 0.43 1 15 2.63 3.65 NA 139 NA Costa Rica 0 0 0 1 4 2.46 3.28 NA NA 68 Colombia 0.5 0.13 0.5 1 7 2.26 1.88 NA NA NA Bolivia NA NA NA NA 9.5 1.61 4.38 NA NA NA 0 0 0 1 5 NA NA NA NA NA Uruguay NA: Not Available Source: Data for the first 4 columns was kindly provided by Carsten Fink, Aaditya Mattoo, and Ileana Cristina Neagu* (2002). 16 Conclusions: A Watch List Africa and Latin America: Out of the Value-Chain Game? The share of China’s total exports produced by foreigners has risen sharply, from 32% to 60% between 2000 and 2005. Foreign outsourcing is becoming a major driver of India’s and China’s high tech exports, both countries moving up quickly in the value added ladder. In 2005 for example, of China’s top 100 exporters, 53 were foreign companies and all were electronics/information technology companies. After China: India? 17 Another Emerging Player from Asia: India’s M&A in 2006 Target Nationality Corus Oil & Gas Assets (Campos Basin) Omnimex de Colombia Oil & Gas Assets (Brazil) Greater Nile Petroleum (25%) Glaceau (30%) Shell Development Angola Oil & Gas Assets (Syria) Betapharm Arzneimittel Hansen Transmissions Eve Holding Terapia Total UK/NL Brazil Colombia Brazil Sudan US Angola Syria Germany Belgium Belgium Rumania Acquirer Tata Group Oil & Natural Gas Oil & Natural Gas ONGC Videsh Oil & Natural Gas Tata tea Oil & Natural Gas Oil & Natural Gas Dr Reddy's Lab Suzlon Energy Suzlon Energy Ranbaxy RECENT INDIAN INVESTMENTS 2006 Deal Value ($m) Corp Corp: China Group Corp Corp Corp: China Group 7700 1670 850 820 783 677 600 581 572 562 548 324 15687 RECENT INDIAN INVESTMENTS (EXCLUDING CORUS-TATA DEAL) 9% 26% 22% US Europe Latin America Africa 13% US Europe Latin America Africa 4% 22% 61% 43% Source: OECD Development Centre. Based on Dealogic and local press. 18 The rise on outward direct investment among emerging economies is remarkable Outward Foreign Investment by country 1999-2007 U$ Millions 30000 25000 Brazil China 20000 India Russia 15000 10000 5000 2007 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 -5000 1999 0 Source: OECD Development Centre. Based on Economist Intelligence Unit, 2007. 19 …helping to the fall of cost of capital Total LatAm outward FDI vs LatAm spreads US$ millions Outward FDI Spreads 45000 40000 35000 30000 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 * Data for 2007 is estimated and includes recent deals Source: OECD Development Centre 2007, based on Thomson Datastream (Economist Intelligence Unit). 20 Thank you Based on: Javier Santiso (ed.). “The Visible Hand of China in Latin America”. OECD Development Centre Studies, 2007. Javier.santiso@oecd.org