Document 17774838
advertisement

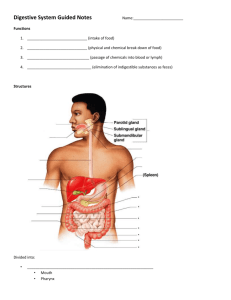
Name:___ ______________ Date: _______Period:_____ Agenda Week of 7 April – 11 April 2008 Unit 6 Physiology Exam 5/13/08 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Monday 4/7/08 - Ch 37 Sci Notebook - Finish HIV/retrovirus infection HW: Study for Unit 6 Quiz 2 Tuesday 4/8/08 (LEAP 2:30 -3:30) - Unit 6 Quiz 2 - Collect Ch 37 Sci Notebook - Ch 37 Study Guide due Thursday HW: Ch. 35 Sci Notebook due 4/16/08 Wednesday 4/9/08 –Late Start - Correct Ch 37 Sci Notebook - Review Quiz #2 Results - Ch 37 Study Guide HW: Ch. 37 Study Guide due Thursday Thursday 4/10/08 – Regular Schedule Parents Night 6:00 – 8:00 pm Correct Ch 37 Study Guide Begin Digestive System Overview Friday 4/11/08 – Minimum Day Periods 1-6 Diagramming Digestive System Unit 6 Quiz 3 4/15/08 1. Cholesterol, sex hormones and large amounts of stored energy are examples of what type of macromolecule? 2. Proteins differ from each other by A B C 3. The wave of muscular contraction that pushes food through the esophagus is called___________________ 4. A digestive function of organ F is the synthesis and secretion of 5-10 Identify the structures A, B, C, D, E, and F Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 4/7/084/11/08. Spring Open House is on 4/10/08 and begins at 6:00. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is ready for the quiz on 4/8/08 and 4/15/08, and has completed all assignments this week. Vocabulary Cholesterol Fatty Acid Pathogen Digestive system Homeostasis Olfactory Insulin Virus Peristalsis Polypeptide I understand if my child needs to retake a quiz that the original quiz with corrected answers, signed by a parent, must be turned in when the quiz is retaken on Tuesday after school. Parent/Guardian Printed Name Signature Date Bell Ringers: Week of 7 April – 11 April 2008 CST Review Questions Monday – Identify Structures 1-7 Tuesday – Vaccinated individuals become protected against polio because the weakened viruses __. A prevent further viral invasion. B induce an inflammatory response. C promote production of antibodies. D are too weak to cause illness. Explain Skeletal structures are common between two animals of different species. These structures probably exist because both species A have a common food source. B live in the same environment. C have survived until the present time. D are related to a common ancestor. Wednesday – The purpose for giving a person a vaccine is to A introduce chemicals that destroy viruses. B stimulate an immune response. C prevent inflammation. D cure a disease. Explain Thursday/Friday – How do nutrients, absorbed by the small intestine, travel to the individual cells of the human body? A The nutrients are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood and move through the circulatory system to the body cells. B The nutrients move from the small intestine directly to the liver and then move through the lymphatic system to the body cells. C The small intestine forces the nutrients into the kidneys, where the nutrients are then dissolved in fluids used by the body cells. D The body cells send nerve impulses indicating a lack of nutrients to the small intestine, and the small intestine sends the nutrients back to the cells. Explain Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______ Unit 6 Quiz 3 April 15 2008 (20 points) 1. The wave of muscular contraction that pushes food through the lower esophagus and the intestines is called _________________ 2. Proteins differ from each other by A) B) C) 3. Cholesterol, sex hormones and large amounts of stored energy are examples of what type of macromolecule? 4. A digestive function of organ F is the synthesis and secretion of 5-10 Identify the structures A, B, C, D, E, and F Extra Credit 1. Vaccinated individuals become protected against polio because the weakened viruses __. A prevent further viral invasion. B induce an inflammatory response. C promote production of antibodies. D are too weak to cause illness. 2. The purpose for giving a person a vaccine is to A introduce chemicals that destroy viruses. C prevent inflammation. B stimulate an immune response. D cure a disease. 3. How do nutrients, absorbed by the small intestine, travel to the individual cells of the human body? A The nutrients are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood and move through the circulatory system to the body cells. B The nutrients move from the small intestine directly to the liver and then move through the lymphatic system to the body cells. C The small intestine forces the nutrients into the kidneys, where the nutrients are then dissolved in fluids used by the body cells. D The body cells send nerve impulses indicating a lack of nutrients to the small intestine, and the small intestine sends the nutrients back to the cells. Vocabulary Matching ____ Cholesterol ____ Digestive system A. A structure composed of modified epithelial cells specialized to produce one or more secretions that are discharged to the outside B. A long carbon chain carboxylic acid; vary in length and in the number and location of double bonds; three linked to a glycerol molecule form fat. _____ Homeostasis C. Rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscle that push food along the digestive tract. _____ Fatty Acid D. An organism or a virus that causes disease. _____ Olfactory E. A steroid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other important steroids. _____ Insulin F. A protein (or protein-based molecule) that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living organism; acts as catalyst for specific chemical reaction. _____ Virus G. The steady-state physiological condition of the body – maintaining conditions. _____ Polypeptide H. The primary function is to convert food into energy and convert waste into excretable material. _____ Peristalsis I. A submicroscopic, noncellular particle composed of a nucleic acid core and a protein coat (capsid); parasitic; reproduces only within a host cell. _____ Pathogen J. having to do with the sense of smell, involves the detection and perception of chemicals floating in the air ____ Enzyme K. A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. ____ Gland L. A vertebrate hormone that lowers blood glucose levels by promoting the uptake of glucose by most body cells and the synthesis and storage of glycogen in the liver; forms in the pancreas.