Cold War
advertisement

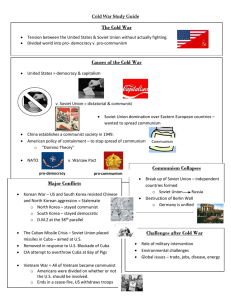
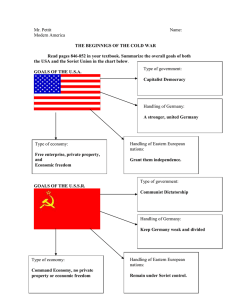
Cold War • Cold War - an atmosphere of suspicion, distrust, rivalry and hostility between the Soviet Union and United States. • Not an actual war, but a collection of conflicts / flashpoints that brought the world to the brink of total war. Cold War Steps leading to the Cold War: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Russian Revolution (1917) – communist overthrow Political Isolation of Russia (20s and 30s) - fear of communism Russian Industrial Revolution during the (30s) – thriving while world depressed Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) – Stalin wanted pro-Soviet gov’ts in Eastern Europe. West opposed to Soviet influence Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – division of Germany and Soviet control of Poland was seen as temporary by West and permanent by USSR Atomic Bomb (1945) – Soviets felt betrayed as US never told them about bomb Soviet Spy Network Publicized (1945) - Gouzenko Cold War Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron Curtain”] US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the GOAL spread world-wide eventual collapse of the Communism METHODOLOGIES: Communist world. [George Kennan] 1. Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] 2. Arms Race [nuclear escalation] 3. Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts of Third World peoples [Communist govt. & command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist economy] “proxy wars” 4. Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact] Cold War • Iron Curtain – boundary between two sides. It blocked free movement of info, products, and people Cold War • Truman Doctrine (1947) – $400 million in economic aid to Greece and Turkey. Hoped this would stop spread of communism • Marshall Plan (1947)– massive aid package that offered food and economic assistance to European countries. Used to strengthen democracies • Keenan’s Policy of Containment – policy to stop the spread of communism following WWII Cold War • Berlin Airlift – In 1948, Soviet Union broke agreement with former allies (and their rights to occupy their share of West Berlin) and formed a blockade (lasts 11 months) • Allies flew in food and supplies • Increased tensions between the powers Cold War Vs. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) Warsaw Pact (1955) Cold War United States Luxemburg } U. S. S. R. } East Germany Belgium Netherlands } Albania } Hungary Britain Norway } Bulgaria } Poland Canada Portugal } Czechoslovakia } Denmark 1952: Greece & Turkey France Iceland Italy 1955: West Germany 1983: Spain Rumania Cold War Arms Race – building military superiority • Soviet Union detonates atomic bomb in 1949 • U.S. develops hydrogen bomb in 1952 • Soviet Union develops hydrogen bomb in 1955 • Soviet Union develops Tsar Bomba (50 megatons – largest ever created) in 1961 Cold War Sir.. Show us the videos Cold War






![The Cold War [1945-1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/017625117_1-e9c48b8702d240bbf3e4177b59399df7-300x300.png)