Module 17 Apr 2015
advertisement

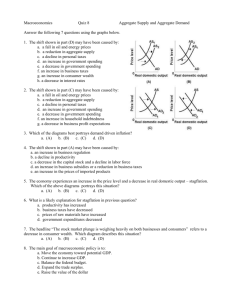
Module 17 Apr 2015 Aggregate demand curve – shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and quantity of aggregate output demanded by households, businesses, the government, and the rest of the world. Movements – up or down – indicate a simultaneous change in the prices of all final goods and services Wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level – is the change in consumer spending caused by the altered purchasing power of consumers’ assets. An increase in the aggregate price level, other things equal, reduces the purchasing power of many assets. ◦ Ex. If price level increases by 25%, $5000 will have the purchasing power of what $4000 did. People will probably cut back on spending. A fall in the aggregate price level increases the purchasing power of consumers’ assets and leads to more consumer demand. The interest rate effect of a change in the aggregate price level is the change in investment and consumer spending caused by altered interest rates that result from changes in the demand for money In response to an increase in the aggregate price level, people try to increase its money holdings, by borrowing or selling assets (like bonds). This reduces funds available to others and drives interest rates up which reduces investment spending. It reduced consumer spending because people save. Changes in expectations – both consumer spending and investment spending Changes in wealth – consumer spending depends in part on the value of household assets – more $, spend more Size of the Existing Stock of Physical Capital – the incentive to spend depends on how much physical capital they already have – the more they have, the less they’ll spend Government policies and aggregate demand – the two main ways the government can influence the aggregate demand curve are through fiscal policy and monetary policy Fiscal policy – the use of taxes, government transfers, or government purchases of goods and services to stabilize the economy Government purchases have a direct effect on the Agg Dem Curve – because of the equation 𝑌 = 𝐶 + 𝐺 + 𝐼 + (𝐸𝑥 − 𝐼𝑚) Tax rates and government transfers affect it indirectly because they influence consumer spending Monetary policy – the central bank’s use of changes in the quantity of money or the interest rate to stabilize the economy When the central bank increases the money in circulation, households have more money – moves Agg Dem Curve to the right When the central bank decreases the money in circulation, households have to borrow – moves Agg Dem Curve to the left 1. Determine the effect on aggregate demand of each of the following events. Explain whether it represents a movement along the aggregate demand curve (up or down) or a shift of the curve (left or right): A. a rise in the int rate caused by a change in monetary policy B. a fall in the real value of money in the economy due to a higher aggregate price level C. News of a worse-than-expected job market next year D. A fall in tax rates E. A rise in the real value of assets in the economy due to a lower aggregate price level F. A rise in the real value of assets in the economy due to a surge in real estate values 1. Which of the following explains the slope of the aggregate demand curve? ◦ I. the wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level ◦ II. The interest rate effect of a change in the aggregate price level ◦ III. The product-substitution effect of a change in the aggregate price level ◦ A. I only ◦ B. II only ◦ C. III only ◦ D. I and II only ◦ E. I, II, and III 2. Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right? A. a decrease in wealth B. pessimistic consumer expectations C. a decrease in the existing stock of capital D. contractionary fiscal policy E. a decrease in the quantity of money 3. The Consumer Confidence Index is used to measure which of the following: A. the level of consumer spending B. the rate of return on investments C. consumer expectations D. planned investment spending E. the level of current disposable income 4. Decreases in the stock market decrease aggregate demand by decreasing which of the following: A. consumer wealth B. the price level C. the stock of existing physical capital D. interest rates E. tax revenues 5. Which of the following government policies will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left: A. a decrease in the quantity of money B. an increase in government purchases of goods and services C. a decrease in taxes D. a decrease in interest rates E. an increase in government transfers 1. a. Draw a correctly labeled graph showing aggregate demand B. on your graph, illustrate an increase in aggregate demand C. list the four factors that shift aggregate demand D. describe a change in each determinant of aggregate demand that would lead to the shift you illustrated in part b