Intro to Thermodynamics What is ∆H What is ∆S
advertisement

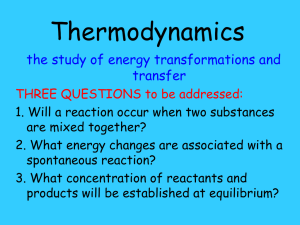
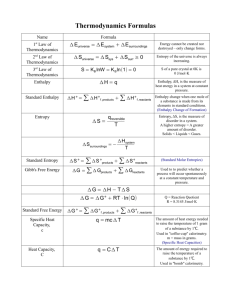
Intro to Thermodynamics What is ∆H What is ∆S A New Term ∆G = Gibb’s Free Energy Energy available to do _______________ due to a particular process. This quantity takes both ___________________ and ____________________ into account Understanding ∆G 1) The real energy available to do _______________ on the ____________________ due to a __________________ or __________________ process (In this case ∆G has a __________________ sign – which means the process is __________________, and occurs all by itself with no net input of energy, and actually gives off energy. This is called an __________________ process) This is ∆G ___ 0. OR 2) The real work energy __________________ to a physical or chemical system in order to cause a particular process to take place (In this case ∆G has a __________________ sign – which means the process is __________________, and does not occur all by itself, requiring a net _______________ of energy in order to take place. This is called an __________________ process) This is ∆G ___ 0. KEEP IN MIND – ∆G takes both Energetic Factors into account 1) Heat (enthalpy ∆H) and 2) Disorder (∆S) A New Equation ∆G = ∆H – T∆S Note: S has units J/K (which means that entropy’s effect on a process is dependent upon the temperature at which the process takes place) Unit analysis: What should be the values for ∆H and ∆S if a negative ∆G is desired? What should be the values for ∆H and ∆S if a positive ∆G is desired? Draw the Thermodynamic TUG OF WAR on the back of this page.