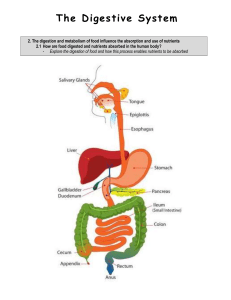
1 (Slide 44) The _______________________ is the major organ of digestion... ___________________ long from ___________________ sphincter to ileocecal valve ....
advertisement

1 Chapter 23 Class Notes Part 2 BSC 2086 Fall 2010 (Slide 44) The _______________________ is the major organ of digestion and absorption; it is ___________________ long from ___________________ sphincter to ileocecal valve . Its subdivisions include: The bile duct and main pancreatic duct join at the _________________________________ ampulla (enlarged area of duct), and enter the duodenum at the major duodenal ______________________ (bump on duodenum); these are controlled by the hepatopancreatic ___________________________. (Slide 49) What are 4 structural modifications of the small intestine and what is their function? (Slide 50) What is a second function of circular folds? What 2 types of cells are contained in the villus epithelium? (Slide 53) Briefly describe microvilli: (Slide 54) What 5 types of cells are contained in the intestinal crypts? What is intestinal juice and what is its function? What is the largest gland in the body? The ____________________________ ligament separates the (larger) right and (smaller) left lobes, and _________________________ the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall. The round ligament is a remnant of the ____________________________ vein running along the free edge of the falciform ligament. (Slide 62) Briefly describe the hepatic, cystic and bile ducts: (Slide 64) Briefly describe a liver lobule: What 3 things are located in the portal triad of the liver? 2 What can be found in the hepatic sinusoids (Slide 66)? (Slide 68) What are 4 functions of hepatocytes? What are the 3 major ingredients of bile, and what is a function of bile salts? What is a major function of the gall bladder? Chapter 23 Part C Briefly describe the Endocrine and Exocrine Functions of the Pancreas: What are 4 enzymes contained in pancreatic juice? Which enzyme is secreted from pancreas in its inactive form? (Slide 6) Protease activation in duodenum: _______________________________ is activated to trypsin by brush border enzyme __________________________________; ______________________________________ and ________________________________________ are activated by _________________________. (Slide 8) What stimulates bile secretion? (Slide 9) Gallbladder contraction is stimulated by _______________________________________________ from intestinal cells exposed to ___________________ and _____________________ in chyme. (Slide18) Chyme contains what 3 things? (Slide 19) What are 3 requirements for digestion and absorption in the small intestine? (Slide 22) What chemical initiates peristalsis? (Slide 26) Describe 3 unique features of the large intestine: What are 4 regions of the large intestine? 3 (Slide 35) What are 2 positive contributions of intestinal flora? (Slide 36) What are 2 main functions of the large intestine? (Slide 41) What are 3 types of chemical digestion? (Slide 42) What are 7 enzymes that digest carbohydrates? (Slide 43) What are 2 ways carbohydrates are absorbed? (Slide 45) What 7 enzymes digest proteins? (Slide 45) How are amino acids absorbed? (Slide 48) What are the 2 steps for digesting lipids? (Slide 49) Describe the steps involved with the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids: (Slide 52) How are nucleic acids digested and absorbed? (Slide 54) How are vitamins absorbed? (Slide 59) What is celiac disease and how is it treated?