Introduction to Nutrition

Introduction to Nutrition
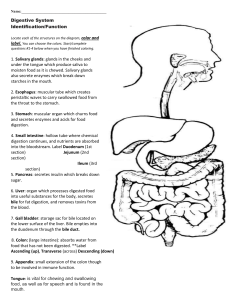
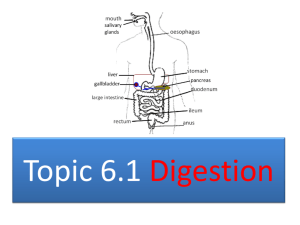
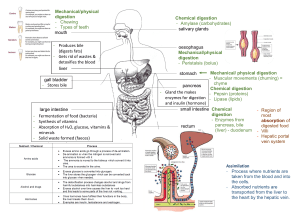
Digestive System:
Gastrointestinal tract:
Absorption
Motility
Feces:
Glandular organs:
While food is in the GI tract it is still part of the external environment
Once absorbed through GI wall nutrients are usable
Four Basic Functions:
Digestion
Secretion
Digestion: From Beginning to End
Mouth:
Oropharynx: posterior mouth, initiates swallowing
Pharynx Esophagus:
Stomach: partially digests food and prepares food for digestion and absorption in s.i.
HCl
(aq)
dissolves most food, not fat and kills bacteria
Pepsinogen secreted proteins
becomes pepsin: begins to breakdown
Amylase: still breaking down carbs
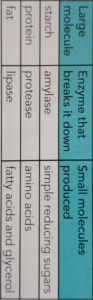
Small Intestine:
Duodenum, jejunum and ileum most absorption occurs in duodenum and jejunum; vitamins, minerals and water are digested by enzymes secreted by the s.i. or liver or pancreas carbs fats
proteins
pancreas: also secretes alkaline fluid to neutralize HCl before it damages the intestinal wall
Liver:
Bile contains, cholesterol, bicarbonate ions (like pancreas), and bile salts (important because they break down fats that are insoluble in water
Gallbladder:
Large Intestine:
Rectum: