Acid Deposition
advertisement

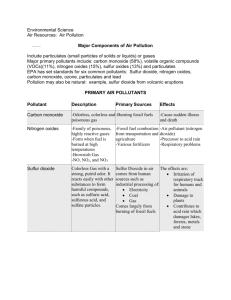
Acid Deposition Acid Deposition • process by which acid-forming pollutants are deposited on Earth’s surface by… – wet- rain, snow, fog – dry- smoke or dust particles • impacts on environment include: – deforestation – increased acidity in lakes and oceans – uptake of toxic minerals by plants or sea life – corrosion of marble, limestone, metals, etc... • precipitation (mostly rain) is the most common form of deposition • rainwater has natural pH of 5.6 – reacts with CO2 to form weak carbonic acid – oyster video (6:07) – CO2 + H2O ⇔ H2CO3 • acid rain –pH < 5.6 –primarily formed from sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NO or NO2) • these oxides dissolve in the rain to make –strong nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) Causes • industrialization – increasing emissions of nitrogen and sulfur oxides – coal burning • volcanic emissions and biological processes Effects of acid rain on structures • limestone and marble contain the base calcium carbonate (CaCO3) • when exposed to acid rain, a neutralization reaction occurs and the building is gradually eroded • makes CaSO4 or Ca(NO3)2 that is more soluble in water than the calcium carbonate • most metals contain iron – iron reacting with sulfuric acid rain (H2SO4) to make FeSO4 Prevention Pre-combustion methods: • techniques used on fuel before combustion • can reduce 80-90% of sulfur before combustion even occurs Post-combustion methods: • techniques used on gases after combustion • remove sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and heavy metals from the gasses before they are released into the air – EX: calcium oxide or lime will react with sulfur dioxide and remove it from the gasses • CaO (s) + SO2 (g) ⇌ CaSO3