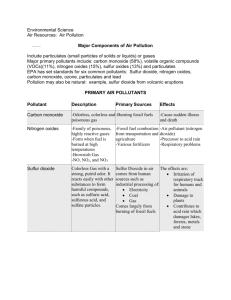
Air pollution refers to the contamination of the air that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere. It occurs when harmful gases, dust and smoke enter the atmosphere. Air pollution leads to diseases, allergies and death. Substances which are responsible for the contamination of air are called air pollutants. Pollutants released into the atmosphere can be of natural origin or man-made. In this unit, the sources and effects of air pollutants concerned are as follows: 1. carbon monoxide 2. sulfur dioxide 3. oxides of nitrogen 4. smoke 5. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The table below refers to the contamination of these harmful gases and smoke which causes harm to living and nonliving things in the environment and the ways to reduce them. 1. Carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide (CO) binds to hemoglobin in the blood and disrupts the oxygen flow in the body. The most common symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning include headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness and death. Carbon monoxide in air cannot be detected as it is a colourless, odourless and tasteless gas. 2. Sulfur dioxide Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a colourless gas with a sharp, irritating smell. Fossil fuels contain sulfur which, on combustion, combines with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide. Thus, sulfur dioxide is released in air from chimneys of factories burning fossil fuels (for example from coal-fired power stations) and exhaust pipes of motor vehicles. Naturally, sulfur dioxide is released into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions. Sulfur dioxide causing acid rain Sulfur dioxide reacts with water vapour and oxygen in the air to form sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid dissolves in clouds, causing rain water to become acidic. This phenomenon is known as acid rain. • Acid rain erodes (eat away) limestone (calcium carbonate rock) buildings • Acid rain corrodes steel structures like cars, bridges, railways and iron roofs. • Acid rain makes water in lakes and rivers more acidic causing fish and other aquatic organisms to die. • Acid rain renders soil acidic and kills plant. 3. CFCs CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) are compounds which are made up of the three elements: carbon, fluorine and chlorine. They are used as coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners, as propellants for aerosol sprays. CFCS and Ozone Depletion The Earth’s atmosphere is surrounded by a layer of ozone which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun preventing them from entering the atmosphere. UV rays cause skin diseases, skin cancers and eye diseases like cataracts. CFCs break down in the atmosphere to form chlorine atoms which react with ozone. Thus, the ozone layer is depleted resulting in holes in the ozone layer. Consequently, harmful ultraviolet rays enter the atmosphere and there is an increased risk of having skin cancers and eye diseases. 4. Oxides of nitrogen Oxides of nitrogen comes from internal combustion engines of vehicles where oxygen and nitrogen from the air react at high temperatures in the engines. The two most common and hazardous oxides of nitrogen are nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Oxides of nitrogen are also formed naturally during lightning. The very high temperature in the vicinity of a lightning bolt causes oxygen and nitrogen in the air to react and form oxides of nitrogen. Oxides of nitrogen react with water vapour and oxygen in the air to form nitric acid, thus causing acid rain. Oxides of nitrogen also have detrimental effects on human health. They damage the lungs and cause respiratory problems. They irritate the eyes and the skin. 5. Smoke The sources of smoke are exhaust pipes of vehicles, chimneys of factories, fires, burning garbage, barbecue grills, burning charcoal and burning cigarettes. Smoke inhalation happens when a person gets trapped in an area, such as a kitchen or home, near a fire. Smoke consists of tiny carbon particles (soot) and ash. Reduced oxygen content in smoke causes suffocation. carbon monoxide in smoke leads to headaches, loss of consciousness and death. Smoke contains acidic gases like sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen which cause irritation of the eyes, skin burns and damage of the lungs. Catalytic converters as a way to reduce the amount of pollutants CO, NO and NO2 Catalytic converters are devices in exhaust systems of cars. They convert harmful gases into less harmful ones. Carbon monoxide is converted into carbon dioxide. Oxides of nitrogen are converted into nitrogen.