Atmosphere & Environment Worksheet: Air, Pollution, Acid Rain
advertisement

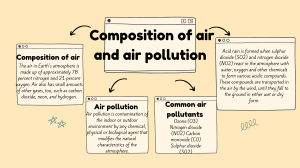
Anderson Secondary School Name: _______________________________ ( ) Date: ___________________ Class: ______________ The Atmosphere and Environment 1.1 Air 1. The _________________ is a layer of air surrounding the Earth. 2. Air is a mixture of several gases. 3. Composition of Air: Gas Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Noble gases (argon, neon and helium) Composition by Volume 79% 20% 0.03% (0 – 5%) 1% 4. As air is a mixture, its composition _______________ from time to time and from place to place. 5. Uses of Air: Uses of Oxygen: (a) Used to aid combustion (b) Used as rocket fuel (c) Used by plants and animals during respiration Uses of Nitrogen: (a) Used to make ammonia in the Haber process (b) Used in the manufacture of stainless steel (c) Used as a coolant for freezing and transporting food products (d) Used to preserve body organs (e) Used to make proteins in plants Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 1 6. Fractional Distillation of Liquid Air Air is first ______________ and compressed into liquid. Liquid air is then separated into its constituents (or fractions) by _________________ ____________________. 7. Test Yourself 17.1, TB, p. 274 200 cm3 of air in syringe A was made to pass over heated copper until the reaction was complete. The gas in syringe B was then allowed to cool to its original temperature. What is the volume of gas collected in syringe B? Answer: Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 2 1.2 Air Pollution 1. _________________________ is the condition in which air contains a high concentration of certain chemicals that may harm living things or damage non-living things. 2. Air pollution is caused by solid particles and poisonous gases in the air. 3. They come from both natural sources and from human activities. 4. With increasing urbanization and industrialization, humans have been releasing more waste into the atmosphere than nature can cope. 5. Common Air Pollutants: (a) Carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide (___________) is a poisonous gas that is colourless and odourless. Natural Sources: Forest fires Man-made Sources: Incomplete combustion of __________________________ fuel. Incomplete combustion of _______________ in car engines. Harmful effects: a. It combines irreversibly with the haemoglobin in the red blood cells to form a compound called ___________________ and thus, reduces the blood’s affinity to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. Breathing in large amounts of carbon monoxide can cause loss of consciousness and even death. b. Breathing in small quantities of carbon monoxide causes ________________, dizziness, breathing difficulties and heart damage. Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 3 (b) Oxides of Nitrogen Oxides of nitrogen include nitrogen monoxide / nitric oxide (_________) and nitrogen dioxide (___________). Natural Sources: Lightning activities (______________________ in the atmosphere causes nitrogen and oxygen to react with each other) Man-made Sources: Formed in internal combustion engines like car engines, power stations and fuel furnaces Formation of Oxides of Nitrogen: 1. Nitrogen combines with oxygen in the air to form nitrogen monoxide (NO). N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) 2. Nitrogen monoxide, a colourless gas, reacts with oxygen to form a brown gas, nitrogen dioxide. 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) Harmful Effects: a. Forms __________________ Increases corrosion rates of buildings and monuments Low pH conditions kill plants and marine creatures b. Causes eye irritation c. Causes breathing difficulties d. Causes inflammation of the lungs (bronchitis) e. Causes greenhouse effects Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 4 (c) Sulfur dioxide Natural Sources: Volcanic eruptions Man-made Sources: Combustion of _______________ (crude oil/petroleum, coal and natural gas) that contain sulfur Formation of Sulfur Dioxide: 1. Sulfur in the fuel burns in oxygen from air to form sulfur dioxide. S(s) + O2(g) SO2(g) Harmful Effects: a. Forms acid rain Increases __________________ rates of buildings and monuments Low pH conditions kill plants and marine creatures b. Causes eye irritation c. Causes breathing difficulties d. Causes inflammation of the lungs (bronchitis) 1.3 Acid Rain 1. The pH value of unpolluted rainwater is slightly below 7. 2. Carbon dioxide in air dissolves in rainwater to form ________________, which is a weak acid. CO2(g) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) 3. Acid rain is formed when acidic air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide __________________ in rainwater. 4. The pH value of acid rain is about __________ or less. 5. Formation of acid rain from sulfur dioxide: a. Sulfur dioxide dissolves in water to form __________________ (H2SO3). SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3(aq) b. In the presence of oxygen in the air, this acid is slowly oxidised to sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 5 6. Formation of acid rain from oxides of nitrogen: a. In the presence of oxygen and water, nitrogen dioxide is converted to _____________. 4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) 4HNO3(aq) 7. Both sulfuric acid and nitric acid are formed in the clouds, and may be carried by the winds and precipitated in the form of snow or rain. 8. Effects of Acid Rain: Acid rain reacts with ___________ and with ______________ in marble and limestone. Metal bridges and stone buildings are damaged. Acid rain can reduce the pH value of natural water bodies to below 4, which will _______ fish and other aquatic life. Acid rain also _____________ important nutrients from the soil and destroys plants by damaging their roots, thus causing deforestation. Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 6 9. Reducing the Effects of Acid Rain Burn fuels which contain little or no ______________ Reduce the amounts of pollutants emitted into the air Use of _______________________ in cars Removal of ___________________ in power stations ___________________ the acids in soil and lakes. Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) is added to soil Calcium carbonate powder is added to lakes. Prepared by Ms. Chen HP Chapter 17: The Atmosphere and Environment 7