Document 17623967
advertisement
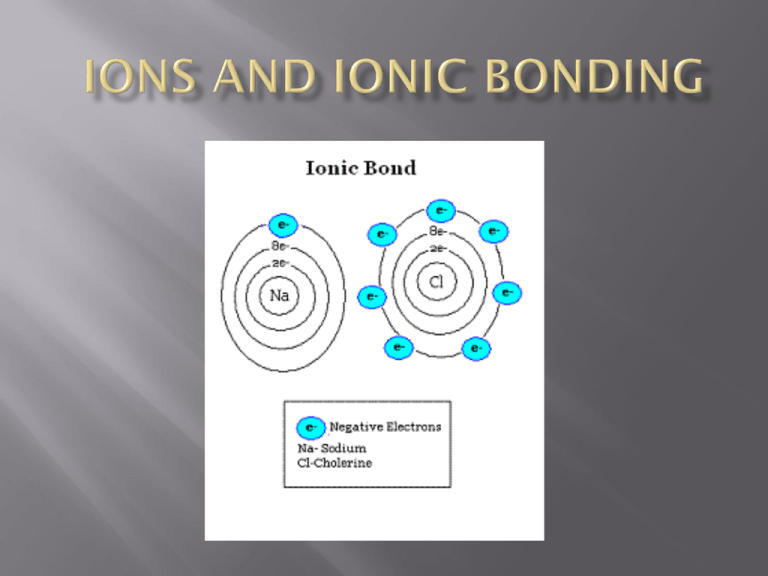
atoms that are now stable because they have gained or lost valence electrons resulting a positively or negatively charged atom a type of chemical bond formed between ions with opposite charges (+ and -) therefore, it is mostly elements from the left side of the periodic table combining with those from the right side + - always the same elements in the same proportion ex- NaCl (1:1) CaCl2 (1:2) Al2O3 (2:3) atoms gain or lose valence electrons in order to have a full valence shell (2 or 8) ex) Na has one valence electron, therefore it would lose it and be 1+ charged ex) O has six valence electrons, therefore it would gain two and be 2- charged e- + - + - Na gives Cl one electron and now both atoms are stable it is easier to just draw Lewis-dot structures to show valence electrons instead of the drawing the whole atom An oxidation number indicates the charge on the atom (or ion) when electrons are lost, gained, or shared in chemical bonds the oxidation numbers for all the atoms in a compound must add up to zero 1+ 2+ 3+ 4+/- 3- 2- 1- 0 ...etc. As it turns out, atoms bond together for a very simple reason: atoms like to have full valence shells (2 or 8). sometimes it takes more than one of each atom to make the compound “work” Mg and Cl? it takes two chlorines to combine with one magnesium MgCl2 → magnesium chloride Mg and N? it takes two nitrogens to combine with three magnesiums Mg3N2 magnesium nitride Easiest way is to switch the charge numbers and write them as subscripts on the formula. Be +2 and N 3Be3 N2 beryllium nitride there is only one way ions can combine, therefore there is only one name for each compound formed keep the first element’s name the same change the second element ending to ide sodium and chlorine (NaCl) becomes… sodium chloride magnesium and fluorine (MgF2)…. magnesium fluoride K and P (K3P) potassium phosphide