The Periodic Table
advertisement

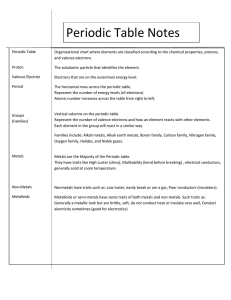
The Periodic Table most of the pure elements are solid at room temperature, only 11 naturally occurring elements are a gas, and only 2 elements are liquid at room temperature Dmitri Mendeleev (1829-1869) • organized a “Periodic Table” (only knew about 63 elements at the time) based on increasing atomic mass – the properties of elements had something to do with their mass • even left empty spaces to be filled in later!!! 3 Main “categories” of elements • Metals – – – – – – – shiny ductile malleable good conductors of heat and electricity have high melting points will corrode (rust) in water or air generally give away electrons • Nonmetals – located to the right of the zig-zag line in the periodic table – often are different from one another – dull – do not conduct heat and electricity – are not malleable nor ductile – have a tendency to gain electrons • Metalloids – elements on the “zig-zag line” – have some characteristics of both metals and nonmetals • Groups are the vertical columns. – elements have similar, but not identical, properties • most important property is that they have the same # of valence electrons Alkali Metals • soft metals • most reactive of the metals because they all lose one valence electron VERY easily http://www.microchem.de/elec000a-k.JPG Alkaline Earth Metals • harder and denser than alkali metals • not as reactive as the alkali metals because have two (out of 8) valence electrons Transition Metals (Elements) • display typical metallic characteristics • give away valence electrons depending what they chemically combine with Halogens • form diatomic molecules – (F2 Br2 I2 Cl2 ) • all gain one valence electron VERY easily Noble Gases • mostly unreactive because their valence level is full (2,8,8….) – do not lose any valence electrons • colorless, odorless gases Tendency to gain valence electrons Mixed Groups • not as similar to each other as other groups • usually named after the first element in the group (B C N O) Rare Earth Elements • not actually rare • some are synthetically produced • used in the nuclear industries, metallurgy, ceramics, electrical components… • Periods are the horizontal rows – may not have similar properties – however, there is a mathematical pattern to their properties as you move across the table 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6 7 radius increases radius increases