Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
advertisement

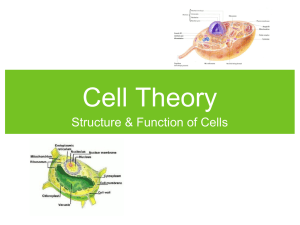
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section 7-1 The History of the Cell Theory and Microscopes Historical View of the Cell Theory • As science improves, so do improvements in scientific instruments, and improved scientific instruments lead to new discoveries. 1590 – Zacharias Janssen • Built first simple microscope (one set of lenses) 1670’s Anton Van Leeuwenhoek • Made improvements • 270x magnification • Saw bacteria, protozoa, sperm cells, red blood cells and yeast cells 1665 – Robert Hooke • Produced a compound microscope • Saw hollow boxes and named them “cells” 1665 – Robert Hooke 1831 – Robert Brown • Saw central structure in plant cells, called this structure a nucleus 1838 – Theodore Schwann • Concluded that all animals are made of cells 1838 – Matthias Schleiden • Concluded that all plants are made of cells 1839 – Johannes Purkinje • Stated that “the cell is the unit of function of life” 1858 – Rudolf Virchow • Concluded that “ cells come only from previously existing cells” The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Section 3-2 Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Eukaryotes • Have a nucleus and membrane covered organelles Prokaryotes • Don’t have a nucleus and membrane covered organelles Eukaryotic Cell Structures Plasma Membrane • Separates the cell from its environment • Controls the transport of materials in and out • Allows some materials but not others to pass through this is called… –Selectively permeable Endoplasmic Reticulum • Extensive network of tube-like structures that forms a passageway that functions in the transport of materials throughout the cells Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis • Attached to the walls of the ER or move freely in the cytoplasm Golgi Bodies • Stack of tiny, flattened sac-like tubes used in secretion • Package protein molecules in a membrane and send the package to the cells surface Mitochondria • Where cellular respiration takes place to release energy • “Mighty Mitochondria” • Powerhouse of the cell Microtubules • Tubes that serve as support for the cell Microfilaments • Thin threads attached to the cell membranes, play a role in movement Lysosomes • Vesicles that contain enzymes used in digestion • Fuses with food vacuoles to digest food into smaller pieces • Digest old cell structures to dispose of them or even entire cells Nucleus • Regulates all the cells activities Chromosomes • Long coiled fibers that carry the material of heredity • Made of protein and DNA Nucleolus • Composed of RNA • Involved in the passage of RNA into the cytoplasm Centrioles • Small cylinders in the cytoplasm that play a role in cell division Cilia Flagella Chloroplasts • Organelle found only in plants, used to make food Vacuoles • Spherical, bubble-like storage sacs • Plant cells have very large vacuoles compared to animal cells Cell Wall • Rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane • Made of cellulose • Permits most things to pass through Cell Wall Section 3-3 Cellular Processes The Big Idea • Cells need to regulate the movement of dissolved molecules on either side of the membrane Cell membrane • Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support Outside of cell Proteins Carbohydrate chains Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer Cell membrane • Made of a double layered sheet called a lipid bilayer Outside of cell Proteins Carbohydrate chains Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer Cell Wall • Provide support and protection for cell • Found in more than just plants • Contrary to popular belief, not selectively permeable Cell Walls Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries • One of the more important functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of dissolved molecules from one side of a membrane to the other Concentration • The mass of solute in a given volume of solution • Mass/volume • What is the concentration of 12 grams of salt in 3 liters of water? • What is the concentration of 12 grams of salt in 6 liters of water? In a solution, particles move constantly Diffusion • Process by which molecules of a substance move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Diffusion Diffusion Equilibrium • When the concentration of the solute is the same throughout a system • Because diffusion depends on random particle movements, substances diffuse across membranes without energy being used • Even during equilibrium, particles still move, but there is no net change in concentration Osmosis • The diffusion of water Osmosis Isotonic • The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell Hypertonic • Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell Hypotonic • Solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell Facilitated Diffusion • Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels •Only go from high concentrations to low concentrations •Does not require energy Glucose molecules High Concentration Cell Membrane Low Concentration Protein channel Types of Active Transport • Sometimes cells must move materials in the opposite direction –Low concentrations to high concentrations Active Transport • Energy requiring process that moves materials across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient Molecule to be carried Active Transport Energy Molecule being carried Molecular transport • Small molecules and ions are actively transported Carrier proteins • Proteins that act like pumps Endocytosis • The process of taking material into the cell by means of infolding of the membrane Food particle engulfing Forms a vacuole Phagocytosis • Cell eating • White blood cells do this Pinocytosis • Cell drinking Exocytosis • Forces contents out of the cell • Endocytosis in reverse Section 3-4 The Diversity of Cellular life Unicellular Organism • Single celled • Do everything a living organism does Multicellular Organism • Many celled • Depend on communication and cooperation among specialized cells Specialization • When cells develop in different ways to perform different tasks Red Blood Cells • Transport oxygen Pancreatic Cells • Make proteins • Packed with ribosomes Skeletal Muscle • Generate force • Packed with mitochondria • Overdeveloped cytoskeleton Nerve Cell • Send messages Guard Cells • Open and close the stomata Levels of Organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Tissues • Group of similar cells that perform specific function • Ex.) smooth muscle Organ • Group of tissues that work together to perform a specific function • Ex.) stomach Organ System • Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function • Ex.) digestive system • This organization creates a division of labor that makes multicellular life possible Biological Organization