World History II SOL Review Great Depression – Cold War
advertisement

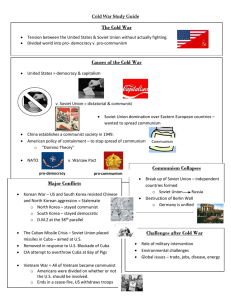
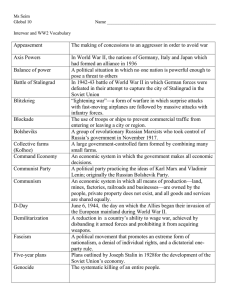
World History II SOL Review Great Depression – Cold War Great Depression - Causes German reparations Buying on credit Overproduction – high supply + low demand = low prices for farm goods and manufactured goods Protective Tariffs – countries passed tariffs (taxes on imports) to make people buy goods produced and food grown in their country (foreign goods were more expensive) Stock Market Crash (October 1929) Great Depression - Results High unemployment Bank failures + collapse of credit Collapse of prices in world trade Growth of Fascism (extreme nationalism) in Italy and Germany Nazi Party blamed Jews for the economic collapse Adolf Hitler Germany Came to power because of inflation and Great Depression (legally came to power) Anti-Semitism Extreme nationalism (fascist) Nazi Party Challenge to world power – sent troops into the Rhineland (demilitarized zone according to Versailles treaty) Benito Mussolini Italy Fascist (1st fascist leader) Wanted to restore the glory of the Roman Empire Challenge to world power – invaded Ethiopia Tojo Japan Militarist Japan’s industrialization – need for raw materials and markets Challenge to world power – invaded Korea, Manchuria, and rest of China World War II - Causes Aggression by totalitarian power (Hitler, Mussolini, and Tojo) Nationalism (Fascism – extreme nationalism) Failures of the Versailles Treaty Weakness of the League of Nations Appeasement – Munich Conference (gave Hitler the Sudetenland to avoid war) Isolationism/Pacifism in United States and Europe World War II – Major Events Began – German invasion of Poland France fell (Britain left alone to fight the Axis Powers) Battle of Britain – bombing of London Operation Barbarossa – German invasion of the Soviet Union U.S. entered war after Japan attacked Pearl Harbor U.S. dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki to end war with Japan World War II – Major Leaders Franklin D. Roosevelt – President of the U.S. Harry Truman – replaced Franklin Roosevelt as president/dropped atomic bomb on Japan Dwight D. Eisenhower – Allied commander in Europe (D Day) Douglas MacArthur – U.S. General in the Pacific Winston Churchill – Prime Minister of England Joseph Stalin – dictator of Soviet Union Hirohito – Emperor of Japan Outcomes of World War II European powers loss of empires (ex. Japan lost territory gained by the war) Two super powers emerged – U.S. and Soviet Union Nuremberg Trial – tried Nazis for war crimes Division of Europe – Iron Curtain (capitalist/democratic vs. communist/totalitarian) United Nations Outcomes of World War II NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) – military alliance that included U.S., Canada, and western Europe Warsaw Pact – Soviet Union and Eastern Europe Holocaust Genocide – the systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, religious, or cultural group Elements leading to the Holocaust – history of anti-Semitism, defeat in World War I and Great Depression blamed on the Jews, Hitler’s belief in a master race, and Final Solution (death camps) Examples of Other Genocides Armenians by leaders of the Ottoman Empire Peasants, government and military leaders, and members of the elite in the Soviet Union by Joseph Stalin (Great Purge) The educated, artists, technicians, former government officials, monks, and minorities by Pol Pot in Cambodia Tutsi minority by the Hutu in Rwanda Muslims and Croats By Bosnian Serbs in Yugoslavia Post World War II - Japan U.S. occupation of Japan led by MacArthur Improved economy Brought democracy to Japan – constitution/elections Japan can only have a military for defense Post World War II – Germany Division of East (Soviet Union) and West (U.S., France, and Great Britain) Division of Berlin (East and West) Democratic government in West Germany Early Cold War Yalta Conference - meeting of three main allied leaders (Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill) + planned "the whole shape and structure of post-war Europe“ + Stalin had the right to control the governments of Eastern Europe (Soviet troops were already stationed throughout Eastern Europe as they pushed toward Germany) Democracy and Capitalism vs. Dictatorship and Communism Truman Doctrine – contain communism (not let it spread) Marshall Plan Rebuild Western Europe (aid and assistance) – prevent the spread of communism Berlin Wall Surrounded city of West Berlin so that people would not escape to West Germany Korean War Cause – North Korea invaded South Korea Result – North Korea and South Korean still divided along 38th parallel China supported North Korea and U.S. supported South Korea Vietnam War Cause - Ho Chi Minh encouraged communist rebels to overthrow South Vietnamese government Results - U.S. troops left Vietnam + unification of Vietnam (communist country) Vietnamization Nixon's administrations policy of building up South Vietnamese forces while gradually withdrawing American troops Domino Theory If Vietnam became a communist country, the countries adjacent to (surrounding) Vietnam would also become communist countries Cuban Missile Crisis Cause – Soviet Union places nuclear missiles in Cuba Results – Soviet Union removed missiles and U.S. promised not to invade Cuba Collapse of Soviet Union Communism failed!! - increasing Soviet military expenses to compete with the United States + economic inefficiency Gorbachev and President Reagan – key leaders Eastern European countries (communist block) wanted independence U.S. encouraged dissidents (people who wanted independence) in communist countries (Poland) Some Warsaw Pact countries joined NATO after collapse of Soviet Union – expansion of NATO Collapse of Soviet Union Establishment of independent states in Eastern Europe and the breakup of the Soviet Union Movement toward a free market economy Fall of Berlin wall and reunification of Germany