Bellringer: 2/18
advertisement

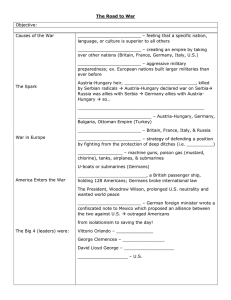
Bellringer: 2/18 Pick up the papers by the door. Please begin working on your SOL Reading and your WWI Vocab. We will take about 15 minutes at the start of class for you to work on these. Write down your HW: Finish WWI vocab to be checked next class for a HW grade. Table of Contents Update: 103: SOL Reading – WWI 104: Notes: WWI Begins 105: Documentary Qs: WWI – The Death of Glory The “War to End All Wars” 1914-1918 Time of Peace 1896 – First Modern Olympics 1899 –Universal Peace Conference Europe 1914 Militarism: glorification of the military. Military Growth Increasing reliance by Monarchs on “military advisors” As tensions increased countries increased troop strength many countries abandoned the “Professional Army” in favor of conscription (the draft) and civilian “Reserve Units” Distrust of one another resulted in… Alliances: An agreement between two or more countries to give each other help if it is needed. When an alliance is signed, those countries become known as “allies”. Sounds like a good strategy, BUT… Downfall: They meant that some countries had no option but to declare war if one of their allies declared war first. Rivalries Between World Powers Develop Over Colonies France & Great Britain Argued over control of Egypt & Sudan – nearly went to war France & Germany Both wanted control of Morocco Germany & Great Britain Germany’s proposed “Berlin to Baghdad Railroad” threatened Britain’s supremacy in the Middle East. Germany & U.S. Nearly went to war over control of Samoa. Rivalries Between World Powers U.S. & Spain – Spanish-American War 1898 – “Manifest Destiny” U.S. gained control of Cuba, Philippine Islands, Guam, Russia & Austria-Hungary Dispute over Austria-Hungary’s annexation of Bosnia & Herzegovina. (1908) Dispute over Russia’s policy of “Pan-Slavism” in the Balkans Austrian opposition of Serbia’s plan for a “Greater Serbia” Alliance Map During WWI Triple Alliance – Central Powers 1882 – Bismarck (Germany) signed a treaty with Italy & Austria-Hungary 1914 – Germany & Austria-Hungary fought together but Italy did not Triple Entente – Allies 1893– France & Russia formed an alliance 1904– France & Britain formed an alliance Britain later signed an agreement with Russia Alliances Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dpu Oa6u6HX0 Nationalism: A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one’s country. Austria/Hungary Hungarians resent Austrian dominance in the Dual Monarchy Slavs in Austria-Hungary agitate for independence. ○ Slavic independence movements supported & encouraged by Serbia Austria-Hungary’s annexation of Bosnia & Herzegovina frustrated Serbian ambitions of expansion. Imperialism: domination by one country of the political, social, economic, or cultural life of another country or region (1850-1914). As industrialization grew, so did the competition for overseas markets. Since the German Empire was not established until 1871, Germany had fallen behind the rest of Europe in the race to win overseas colonies. Assassination: the targeted killing of a public figure may be prompted by religious, ideological, political, or military reasons. Who was Archduke Francis Ferdinand? heir to throne of Austria-Hungary perceived as “weak” disliked by the Hungarians not respected by Austrians because he married a low-level Polish princess sent to visit politically unstable province of Bosnia Slav “nationalists” carry out demonstrations, civil disturbances, bombings & assassinations in Bosnia & Herzegovina in an effort to gain independence from Austria-Hungary “Secret Societies” Within Serbia The “Black Hand” a secret Serbian revolutionary society trains & arms “nationalists” inside Bosnia. Serbian government officially denies involvement in any secret Revolutionary societies. Sarajevo June 28, 1914. Gavrilo Princip fires two shots killing Ferdinand and his wife. STUMBLING TO WAR KAISER WILHELM II (horrified at assassination, urges war) BLANK CHECK (offered from Germany to Austria-Hungary) ULTIMATUM (crush anti-Austrians & punish officials) JULY 28, 1914: Austria declares war on Serbia CZAR NICHOLAS II (asked Wilhelm to ease up) MOBILIZATION (Russia begins to prepare its troops) The powder keg is sparked Declares War On… Austria-Hungary Serbia Russia France Germany Declares War On… Austria-Hungary Serbia Russia France Germany Germany Britain Western Front Schlieffen Plan: German strategic plan of attack of fighting along two fronts for a quick victory. Attack France first to the west, attack Russia second to the east. FAILED because: Russia mobilized faster than expected. Germany shifted troops from western to eastern front. British and French troops pushed back German forces along the Marne River. War Plans Developed Germany invades neutral Belgium to get to France Britain had guaranteed Belgian neutrality Reaction of the People Britain = labor unrest Russia = Revolution of 1905 War brought temporary relief to these countries Young men rushed to enlist and fight for justice and a better world Sinking of the Lusitania What was the Lusitania? A British ocean liner that sailed across the Atlantic What happened to it? It was torpedoed by a German U-boat Was carrying passengers from many nations (including the U.S.) Sinking of the Lusitania NOTICE! “Travelers intending to embark on the Atlantic voyage are reminded that a state of war exists between Germany and her allies and Great Britain and her allies; that the zone of war includes the waters adjacent to the British Isles; that, in accordance with formal notice given by the Imperial German Government, vessels flying the flag of Great Britain, or any of her allies, are liable to destruction in those waters and that travelers sailing in the war zone on ships of Great Britain or her allies do so at their own risk.” IMPERIAL GERMAN EMBASSY WASHINGTON, D.C., APRIL 22, 1915. https://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=M5z4I3aIn7E U.S. ENTRY INTO WWI REASONS Unrestrictive submarine warfare (Lusitania) Zimmerman Telegram SELECTIVE SERVICE ACT requires young men to enlist 400,000 enlist 18-45 years old PERSHING wants to fight in traditional way— horses; ends up in the trenches Contrast with WWI Technology New Weapons Used in War What do you see here? Why might the soldiers be wearing gas masks? How are machine guns different from older guns? How might machine guns affect military strategy? Machine guns and Submachine guns (Automatic rifles) Flamethrowers Kleinflammenwerfer Grossflammenwerfer Armored Cars Trench Warfare Trench Warfare Trench Warfare emerged in the first few months of WWI due to heavy machine gun and artillery fire used as shelter and survival from constant enemy fire dug in a zigzag pattern cramped, muddy, wet, rat infested, disease prone (trench foot), and dull – HORRIBLE!! Viewer Discretion is Advised! Typical WWI Trench Layout This aerial photograph shows the way in which the battlefield was set up. In between the front lines lies “no-man’s land,” and also visible is the zig-zag pattern of the trenches, made such that an enemy could not enter and begin firing straight down the entire length of the trench. Communication trenches run back to the second and third lines, and then right back to the rear. The white marks are shell holes. http://www.worldwar1.com/tlbtw.htm Airplanes Airplanes First used to observe enemy troop movements “scouting.” As technology developed throughout WWI, planes became faster and more capable of carrying heavy bomb loads. Pilots known as “flying aces” confronted one another in mid-air battles known as “dogfights.” In 1915, Germany used zeppelins, large gas filled balloons to bomb the English coast. Zeppelins Tanks GAS—mustard gas Chemical warfare Used first by Germany and then the Allies in 1915. Poisonous gas blinded or choked its victims or caused agonizing burns and blisters, even death. Dangerous to everyone because winds often shifted blowing the gases in all directions. Gas masks were used by soldiers to protect their lungs from being poisoned. Gas Masks Motorcycles WWI Listening Radio Listening Devices Radio reporting news of WWI Parachutes Submarines German U-Boats Battleships Dreadnaught Battleships WWI was supposed to be a “quick war,” but with daily advances in technology most battles ended in stalemate with tens to hundreds of thousands of soldiers dying… Casualties of Modern Weaponry Tactics of sending masses of men toward enemy didn’t work against modern weapons British suffered 57,470 casualties on the first day of the Battle of Somme Total losses for World War I exceeded 10 million A new kind of war: Life on the Front Lines of WWI The Reality of Soldier’s Lives War takes a toll on soldiers “war of attrition” Once, young and eager soldiers proud to serve their country, now had little faith in their cause. Some soldiers were mentally or physically wounded while many others lost their lives. Effects of the War of the Home Front Wartime Propaganda Women and the age of “Total War” Women poured into the workforce replacing men who went off to war Jobs: Ran farms Factory workers Office assistants Nurses Women continued Middle and upper class women: paramilitary organizations 40,000 nurses Cooks Drivers Mechanics 13,000 Women’s Land Army Women’s Wages and Changing Roles Paid less than men After the war, women were “demobilized” to make room for men in their jobs. Women discovered benefit of financial autonomy Some refused to return to domestic service Women won the right to vote throughout Europe Wartime economics WWI left the world financially stressed To finance war costs governments: Raised taxes Took out loans Rationed food, clothing, gasoline Set prices Forbid strikes Forced civilian labor Enforced “drafts” Mobilizing for Total War Citizens back home made huge sacrifices (“Victory Gardens”) Governments controlled industries, rationing The War Ends Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire were first Central Powers to be defeated Revolts inside Austria-Hungary and Germany helped end the war quickly November 11, 1918 11 A.M. Armistice Day! Propaganda Poster - PROJECT During WWI almost every other nation involved in the war participated in propaganda advertising to garner (gain) support for the war effort. Propaganda tried to encourage the people to participate in the war effort in some form. Propaganda art usually only outlines some of the facts in order to make a point. Propaganda Poster - PROJECT WHAT YOU NEED TO DO: Create propaganda poster that would have appeared at the post office, grocery store, bank or any other public place during WWI. When creating the poster consider the following: Color: Is it patriotic or just colorful and eye catching? Words: Who is the poster speaking to…rich intellectuals, small children, or someone in between. Symbols: Are there any symbols that mean or stand for other things. (e.g. an eagle is a symbol of freedom) Message: Simple……..what is it going to say? Audience: Who are you addressing in your poster? Who do you want to be reading this poster? Purpose: Which branch of the military or government agency is this poster created to support? Propaganda Poster - PROJECT REQUIREMENTS: Must work by yourself to complete the poster. Must contain at least 1 image. Must contain a reference to a particular nation Must contain correct information about WWI. (1914-1918) Page 2 of notes The Paris Peace Conference Meeting at Versailles: In 1919, the Big 4 met in Paris to negotiate the Treaty; Lloyd George of Britain, Orlando of Italy, Clemenceau of France, and Woodrow Wilson of the U.S. Russia was not invited Central Powers were given a small role Paris Peace Conference Dominated by the leaders of the four major Allied Powers: Woodrow Wilson (U.S.) David Lloyd George (Britain) George Clemenceau (France) Vittorio Orlando (Italy) “The Big Four” What They Wanted: France Great Britain America Italy Georges Clemenceau Lloyd George Woodrow Wilson Vittorio Orlando 14 Points designed to establish lasting peace in Europe Territory Make Germany pay! Similar to French but worried it was too harsh Germany has to be stopped from invading again Treaty might cause hostility in the future Revenge Wilson’s Plan for a Lasting Peace: Woodrow Wilson with the American Peace Commissions in Paris to negotiate the Versailles treaty The 14 Points: Self-determination: boundaries decided based on people & they establish their own governments Mandate System: Colonial policies should consider the interests of the people Freedom of Seas: open trading to all peaceful nations, remove tariffs League of Nations: to provide peaceful means of solving disputes rather than war No secret treaties or alliances formed Arms should be reduced Sooooo…. Treaty of Versailles Signed June 28, 1919 Made Germany agree to a “Guilt Clause” Pay war reparations of $33 Billion Carved large chunks of territory from Germany and placed many restrictions on the German government. Provided for the formation of the League of Nations. Germany’s Restrictions Not allowed to manufacture heavy artillery, tanks, or airplanes. Navy could have FEW warships, but NO submarines. Rules/Restrictions meant to ensure Germany was unable to start a war. Allies lacked ability to enforce imposed restrictions. Territorial Changes at Germany’s Expense Alsace-Lorraine returned to France. Belgium gained some small territories along its boarders. Poland restored as an independent nation. Rhineland Was to be kept free of German military and weapons Allied troops occupied it Weakness’ of the Treaty Germany was humiliated and destroyed Allies ignored the needs of the new Soviet Government International instability was created in the new nations and mandates U.S. returned to isolationist policies America Opposed the Treaty Felt it was too lenient Objected to foreign policy decisions being made by international organizations Senate refused to ratify the treaty & join the League Results of WWI: Bolshevik Revolution in Russia Colonies’ participation in war increased demands for independence. End of Russian Imperial, Ottoman, German and Austro-Hungarian empires U.S. - economic giant More RESULTS of WWI: 10 million soldiers and 10 million civilians are DEAD=20 million Europe and its colonies are devastated Allies won the war, but lost hopes for peace Spanish Influenza spread during war—20-100 million died (estimated) worldwide Empires broken up—mandates made in the Middle East MANDATES – territory under temporary control Ottoman Empire is GONE France and Great Britain divide former Ottoman Empire Britain- Iraq, Transjordan, and Palestine France Syria and Lebanon THIS DIVISION PLANTED SEEDS FOR FUTURE CONFLICT IN THE MIDDLE EAST!!! Destruction never seen before Many towns across Europe lay in ruin due to widespread destruction by mechanized warfare. Families suffered great losses both human and material. The once great Austro-Hungarian Empire now lay destroyed. The political shape of Europe was forever changed. http://www.the-map-ashistory.com/demos/tome03/index.p hp Europe 1914 Europe 1918