The Road to the Great War WWI
advertisement

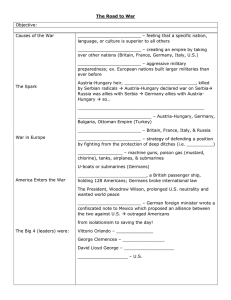
The Road to the Great War WWI Causes of the War nationalism – feeling that a specific nation, language, or culture is superior to all others imperialism – creating an empire by taking over other nations (Britain, France, Germany, Italy, U.S.) militarism – aggressive military preparedness; ex. European nations built larger militaries than ever before The Spark Austria-Hungary heir, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, killed by Serbian radicals Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia Russia was allies with Serbia Germany allies with Austria-Hungary so… Germany declares war on Russia Central Powers – Austria-Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria, Ottoman Empire (Turkey) Allied Powers – Britain, France, Italy, & Russia War in Europe trench warfare – strategy of defending a position by fighting from the protection of deep ditches (i.e. bunkers) technology – machine guns, poison gas (mustard, chlorine), tanks, airplanes, & submarines U-boats or submarines (Germans) America Enters the War German U-boat sank the Lusitania, a British passenger ship, holding 128 Americans; Germans broke international law The President, Woodrow Wilson, prolonged U.S. neutrality and wanted world peace Zimmerman telegram – German foreign minister wrote a confiscated note to Mexico which proposed an alliance between the two against U.S. outraged Americans from isolationism to saving the day! The Big 4 (leaders) were: Vittorio Orlando – Italy George Clemencea – France David Lloyd George – Great Britain Woodrow Wilson – U.S. SUMMARY QUIZ TIME http://www.history.com/sh ows/the-worldwars/videos/trial-byfire?m=5189717d404fa&s= All&f=2&free=false 1. What event ignited the Great War? 2. What kind of warfare dominated the front lines in WWI? 3. Name two reasons why the U.S. enters WWI.