EX 7. Non-current Financial Assets and liabilities – Exercises
advertisement

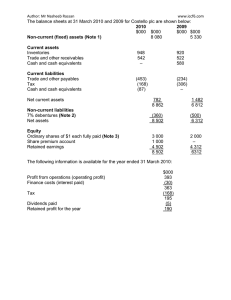
EX 7. Non-current Financial Assets and liabilities – Exercises 1. What is a Financial Instrument? 2. Give some examples of current and non-current assets and liabilities that are financial instruments. Assets Liabilities Current Non-current 3. Financial instruments should be recorded on initial recognition at Fair Value. What does this mean and what are the three levels of inputs to this specified in IFRS 13? 4.How are the following types of financial instruments required to be subsequently measured? a) Financial assets held for trading b) Financial liabilities held with the intention of holding till maturity in order to collect the cash flows c) Investments in other companies held for strategic purposes and classified as Available for Sale. 5. Calculate the Amortized cost of the following Loan. Nominal value $ 1,250 4.7% interest, maturity December 2018 Purchase price $ 1,000 in December 2013 IRR is calculated as 10% Amortized cost Interest income at start of year Cash flows Amortized cost at end of year 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 A 860454 Accounting & Financial Reporting Paul G. Smith 6. How should a company account for a Compound Financial Instrument? 7. Companies use derivative contracts to mitigate their exposure to the market risks associated with financial instruments. Describe the three types of market risk that they seek to manage. 8. What are the three types of hedges that companies use to manage the risks associated with the financial instruments that they hold. Describe each of these and the risks that they are designed to mitigate. 9. How are changes in the fair value of derivative financial instruments designated as hedges accounted for? Describe this for each of the three types of hedge. 10. Which of the following give rise to a financial instrument? a) a credit sale transaction b) A firm commitment to purchase or sell goods or services at a future date c) A forward contract to purchase a commodity at a specific price at a future date d) An option to purchase or sell goods at a future date for a specific price e) A planned future contract A 860454 Accounting & Financial Reporting Paul G. Smith