WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN
advertisement

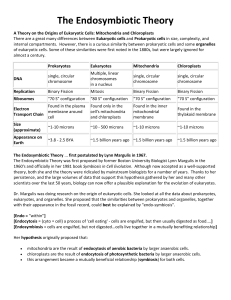
WOODLAND HILLS HIGH SCHOOL LESSON PLAN SAS and Understanding By Design Template Name Matcuk/ Grischow week: Date 01/21/13 Length of Lesson 12 daysContent Area Biology Edline was updated this My Class website was updated this week: STAGE I – DESIRED RESULTS LESSON TOPIC: Cell Structure BIG IDEAS: (Content standards, assessment anchors, eligible content) objectives, and skill focus) • Describe how the property of water supports life on Earth. • Describe and interpret relationships between structure and function at various levels of biochemical organization. • Explain how enzymes regulate biochemical reactions in a cell. UNDERSTANDING GOALS (CONCEPTS): Students will understand: • Describe the unique properties of water and how these properties support life on Earth (e.g., freezing point, high specific heat, cohesion). • Explain how carbon is uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules. • Describe how biological macromolecules form from monomers. • Compare cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. • Describe the fundamental roles of plastids (e.g., chloroplasts) and mitochondria in energy transformations • Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. . VOCABULARY: Atom, lipid, protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrate, enzyme, chemical bonding, prokaryote, eukaryote, chloroplasts, mitochondria, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms, microscope, resolution, magnification, light microscope, nucleus, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, nucleus, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, vacuole ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: • Describe how the property of water supports life on Earth. • Describe and interpret relationships between structure and function at various levels of biochemical organization. • Explain how enzymes regulate biochemical reactions in a cell. • Describe relationships between structure and function at biological levels of organization. • Identify and describe the cell structures involved in processing energy. • Identify and describe the cell structures involved in transport of materials into, out of, and throughout a cell.? STUDENT OBJECTIVES (COMPETENCIES/OUTCOMES): Students will be able to: • How do the properties of water affect life on Earth? • Why lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids are are necessary for human life? • What is the relationship between the structure and function at biological levels of organization? •What are the cell structures and what does each of them do? • What is the structure involved in regulating the transportation of materials in and out of the cell and how does it accomplish this? STAGE II – ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE FORMATIVE ASSESSMENTS: #1. Summarizing Main Ideas #2. Graphic Organizers #3. Exit Tickets Others: PERFORMANCE TASK: • Cell Project STAGE III: LEARNING PLAN INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURES: MATERIALS AND RESOURCES: INTERVENTIONS: ASSIGNMENTS: • Student portfolio • Review of cell parts and Active Engagements used: #1. Higher Level Thinking Skills #2. Partnering Others: Describe usage: • Students will identify the different organelles and cell structures and explain the role they play in the function of the cell. • Projector • Power Point • Lap top • DVD • Worksheets • Lab Equipment • Stem cell video clips CONTENT AREA READING: Chapter 3 Scaffolding used: #1. Build on Prior Knowledge #2 . K-W-L Others: Describe usage: • The student will build on his knowledge of the characteristics of living things learned in Chapter 1. • They will use what they know and what they want to learn about different organisms and the elements found in those organisms. • Discover how the 3 parts of the cell theory came about; determine why cells must be relatively small; compare the structure of prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells; describe the structure of cell membranes. Other techniques used: Prompting if necessary. MINI LESSON: • The Cell PowerPoint • Test Corrections • Extended time for homework and tests • Alternative assignments • Tutoring • College Access organelles and their functions. • Color plates